4 Steps On How To Become An Administrative Lawyer
To become an administrative lawyer, one must earn a bachelor’s degree, excel on the LSAT, enroll in an ABA-approved JD program specializing in administrative law, and pass the Bar Exam. Administrative lawyers must gain experience through internships, networking with professionals, and staying updated on legal precedents, which are crucial steps. The pathway ensures expertise in navigating the complexities of administrative law and government regulations.
An administrative lawyer, an administrative law attorney, specializes in the laws governing government agencies and their interactions with individuals and businesses. The administrative lawyers ensure compliance with administrative policies and challenge or defend decisions made by governmental bodies. The administrative lawyer’s role is crucial for maintaining the balance of power within the legal system, ensuring that regulations are applied fairly and effectively.
Becoming an administrative lawyer typically requires a minimum of 7 years after high school: 4 years to obtain a bachelor’s degree and 3 years to complete a Juris Doctor (JD) degree from a law school. Success on the Law School Admission Test (LSAT) is necessary before law school admission. Earning a JD leads to the crucial step of passing the Bar Exam in the relevant jurisdiction, with further investment in time for specialized experience or education in administrative law being essential.
Excelling as an administrative lawyer and gaining hands-on experience through internships or legal employment in relevant government or private sectors is indispensable. Networking with established professionals in the field opens doors to mentorship and career opportunities. Staying updated continuously on legal precedents and administrative issues is essential for providing informed legal advice and advocacy.
Administrative lawyers must possess strong analytical and research abilities to navigate complex legal frameworks and regulations. Effective communication skills are vital for articulating legal arguments and advising clients or government entities. Attention to detail and critical thinking are paramount in scrutinizing administrative procedures and policies to ensure justice is upheld within the administrative sphere. An example of administrative law involves the review of a regulatory agency’s decision, showcasing the intersection of law and government regulation.
To become an administrative lawyer, follow the 4 steps below.

- Obtain a Bachelor of Law Degree. Obtaining a Bachelor of Law Degree is the first step to becoming an administrative lawyer. The degree lays the foundation of legal knowledge and skills essential for a career in administrative law, providing a comprehensive understanding of administrative processes’ legal principles.
- Take the LSAT. Taking the LSAT is a critical step for aspiring administrative lawyers in assessing their readiness for the rigors of law school. The standardized test evaluates the analytical reasoning and logical skills necessary for navigating the complexities of administrative law, making it a pivotal milestone in their legal education journey.
- Apply to an ABA-Approved Law School. Applying to an ABA-approved law school is crucial for aspiring administrative lawyers. The institutions offer programs that meet the high standards of the American Bar Association, providing opportunities for deep exploration of administrative law and practical experience through specialized courses and internships.
- Take and Pass State Bar Exams. Taking and passing the State Bar exam is the final step to becoming a licensed administrative lawyer. The challenging assessment verifies legal expertise and ability to apply it within administrative law, officially granting the credentials to practice as an administrative lawyer in the jurisdiction.
Table of Contents
- 1. Obtain A Bachelor Of Law Degree
- 2. Take The LSAT
- 3. Apply To An ABA-Approved Law School
- 4. Take And Pass State Bar Exams
- What Is An Administrative Law?
- What Is An Administrative Lawyer?
- What Does An Administrative Lawyer Do?
- How Long Does It Take To Become An Administrative Lawyer?
- When Are Administrative Lawyers Needed?
- How Much Is The Salary Of Administrative Lawyers?
- What Are The Benefits Of Administrative Lawyers?
- What Are The Downsides Of Administrative Lawyers?
- What Are The Skills Required As Administrative Lawyers?
- How Do Administrative Lawyers Differ From Other Lawyers?
1. Obtain A Bachelor Of Law Degree
Obtaining a Bachelor of Law Degree (LL.B.) is the foundational step toward becoming an administrative lawyer. The academic credential equips students with a broad understanding of legal principles, preparing them for a career in navigating and applying administrative law. Majors such as Political Science, Public Administration, or Legal Studies are particularly beneficial for individuals aspiring to the specialty.
One must first complete an undergraduate program to embark on a career as an administrative lawyer, ideally in Law or Public Administration. Success on the Law School Admission Test (LSAT) is a critical next step in evaluating essential reasoning skills for law school. Applying to and being accepted into an accredited law school follows, where a comprehensive 3-4 year curriculum awaits. The curriculum covers various legal disciplines, including disciplines directly relevant to administrative law, ensuring a well-rounded education tailored to the needs of an aspiring administrative lawyer.
The importance of aspiring administrative lawyers, obtaining a Bachelor of Laws (LL.B.) degree is crucial. The degree provides foundational legal knowledge for effectively understanding and applying administrative law. The Bachelor of Laws equips students with critical thinking and analysis skills for navigating legal challenges. The LL.B. is a prerequisite for the bar exam, essential for legal practice. Specialized courses in the LL.B. program deepen understanding of administrative law, preparing students to successfully represent clients before government agencies.
Earning a Bachelor of Laws (LL.B.) degree marks the beginning for aspiring administrative lawyers, who must undertake further steps, including practical experience, advanced education, and professional networking, to specialize in their field. Gaining practical experience through internships or clerkships focusing on administrative law is invaluable, offering insights into the workings of government agencies and the regulatory environment. Advanced legal education, such as a Master of Laws (LL.M.) in administrative law, enhances expertise and career prospects. Networking with professionals in the field and joining relevant legal associations provide mentorship and career advancement opportunities.
2. Take The LSAT
Taking the Law School Admission Test (LSAT) is a pivotal step for students aiming to become administrative lawyers. The LSAT assesses critical skills needed in law school and beyond, such as reading comprehension, analytical reasoning, and logical thinking. A high score is essential for admission into reputable law schools, a prerequisite for a career in administrative law. The LSAT serves as a benchmark for academic capability and readiness for the challenges of legal education.
Registering for a test date through the Law School Admission Council (LSAC) is the first step individuals must take to sit for the LSAT and become an administrative lawyer. Preparation must involve extensive study using official practice tests, prep courses, and study guides to enhance crucial skills. The LSAT, administered at designated centers, includes sections on reading, reasoning, and a writing sample. Scores are reported within weeks after the exam, playing a significant role in law school admissions and, by extension, launching a career in administrative law.
The LSAT is important for aspiring administrative lawyers, serving as the key gateway to law school. The LSAT exam rigorously tests the skills individuals rely on daily as an administrative lawyer, such as critical thinking and problem-solving. Acing the LSAT boosts the chances of getting into a top law school. The LSAT puts scholarship dollars within reach, making it a cornerstone in becoming a standout administrative lawyer.
A high LSAT score furthers one’s ambition to become an administrative lawyer. It opens doors to top-tier law schools known for their rigorous administrative law programs. These institutions often provide unparalleled opportunities for specialization, internships, and networking within administrative law. Preparing for the LSAT allows candidates to refine their critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are indispensable for an administrative lawyer dealing with the intricacies of government policies and procedures.
3. Apply To An ABA-Approved Law School
Applying to an ABA-approved law school is essential for aspiring administrative lawyers. The American Bar Association (ABA) sets comprehensive standards law schools must meet to earn accreditation. Attending an ABA-approved school is pivotal for administrative lawyers, as it ensures that legal education meets the high standards required for professional practice. The step is foundational in preparing for a successful career in administrative law, providing the necessary legal knowledge and skills.
Enrollment in an ABA-approved law school is essential for individuals pursuing a career as an administrative lawyer. Start by researching schools with strong administrative law programs, considering their curriculum, faculty expertise, and placement success. Ensure the individuals meet the requirements, which typically include a competitive LSAT score and a solid undergraduate GPA. Compile a comprehensive application packet with personal statements, recommendation letters, and transcripts. Interviews, when required, offer a chance to highlight the dedication to administrative law. The process lays the foundational steps towards achieving the goal of becoming an accomplished administrative lawyer.
The importance of applying to an ABA-approved law school is vital for individuals who want to become administrative lawyers, as it ensures a standard of education recognized across the United States. The ABA-approved law schools adhere to rigorous criteria set by the American Bar Association, which is essential for ensuring that future administrative lawyers receive a comprehensive legal education. The education equips future administrative lawyers with the knowledge and skills to navigate the complex regulatory environment effectively, laying a solid foundation for a legal career.
Attending an ABA-approved law school opens significant opportunities for aspiring administrative lawyers. The benefits include access to specialized courses in administrative law, internships with government agencies, and networking events with professionals in the field. The experiences are invaluable for building a career in administrative law, providing practical insights and connections that greatly enhance one’s career prospects. Choosing a law school is a crucial decision for future administrative lawyers, directly impacting their ability to succeed in the specialized area of law.
4. Take And Pass State Bar Exams
Taking and Passing the State Bar Exam is mandatory for anyone aspiring to practice as an administrative lawyer. The comprehensive assessment evaluates a candidate’s knowledge and skills in various legal areas, ensuring candidates are prepared for the professional responsibilities of legal practice. Taking and Passing the State Bar Exam is the ultimate step in securing a license to practice law within a specific jurisdiction.
Begin by confirming eligibility through the state’s bar association, requiring graduation from an ABA-approved law school to take and pass the State Bar Exam as an aspiring administrative lawyer. Register for the exam well in advance, and dedicate significant time to studying with bar prep courses, practice tests, and study guides. The exam typically spans several days, covering general legal principles and state-specific laws. Success hinges on thorough preparation and understanding of the law.
The importance of passing the State Bar Exam is crucial for becoming an administrative lawyer, as it not only grants the license to practice law but affirms one’s legal proficiency and ethical standards. The achievement opens doors to career opportunities within administrative law, including positions in government agencies, private firms, and nonprofits. It’s a testament to one’s dedication and competence in the legal field, laying the foundation for a successful and impactful career in navigating and applying administrative law.
The format of the State Bar Exam varies by jurisdiction but generally includes multiple-choice questions, essays, and practical tasks. Effective preparation strategies involve creating a detailed study plan, engaging with study groups or mentors, and utilizing various prep resources tailored to the exam’s format. Undergoing a character and fitness review is part of the process, ensuring candidates meet the ethical requirements for practice. Overcoming the hurdle is a significant milestone, marking the transition from law student to practicing administrative lawyer.
What Is An Administrative Law?
Administrative law is the framework that governs the actions of government agencies, ensuring they act with fairness, transparency, and accountability. Administrative law functions as the agency’s rulebook, defining how government agencies exercise their powers in compliance with democratic values. The branch of law, crucial for an administrative lawyer, bridges the gap between legislative bodies creating laws and executive agencies implementing them. The administrative law definition encapsulates that government operations must be conducted within a legal framework, ensuring that the administration acts according to the law and upholds democratic principles.
The essence of administrative law is defined by its 3 core functions: rulemaking, adjudication, and enforcement. Agencies create and implement regulations that interpret and expand upon legislative statutes through rulemaking, a process where the guidance of an administrative lawyer is vital. Adjudication allows agencies to hold hearings and make decisions affecting individuals or businesses, often with administrative lawyers playing key roles in representing clients. Enforcement in administrative law focuses on investigating and penalizing violations of regulations or laws, another area where administrative lawyers are essential in ensuring justice and compliance. Various agencies carry out the functions at both the federal and state levels, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and state Departments of Motor Vehicles (DMVs).
Understanding “what is administrative law?” is crucial for recognizing its role in maintaining a balance of power within the government, protecting citizens’ rights, and ensuring efficient governance. Administrative law empowers agencies to respond swiftly to complex societal issues while holding them accountable for their actions. The expertise of an administrative lawyer becomes invaluable within the context of administrative law, ensuring that agencies’ actions adhere to legal standards and principles.
Administrative law is indispensable for a functional democracy. Administrative law ensures that government agencies operate within the bounds of law and safeguard the rights of citizens by providing mechanisms to challenge unfair or unjust administrative decisions. The dual focus on efficiency and accountability underscores the importance of administrative law in our daily lives, making it a cornerstone of public law. The framework empowers administrative lawyers to advocate for justice and transparency in the governmental process.
What Are The Types Of Administrative Law?
The types of administrative law encompasses 3 primary types based on the agency’s function: rulemaking, adjudication, and enforcement. An administrative lawyer plays a crucial role across these pillars, ensuring government actions are transparent, fair, and accountable in the legal landscape.
Rulemaking is the process by which administrative agencies create new regulations, a key area where the expertise of an administrative lawyer is often crucial. The regulations interpret and implement legislative statutes, guiding the conduct of both the public and the private sectors. Rulemaking incorporates democratic principles by allowing stakeholders to contribute to the regulatory framework through public notices, comment periods, and hearings.
Adjudication refers to the agency’s resolution of disputes, where the role of an administrative lawyer is often pivotal. The process involves evidence presentation, witness testimonies, and legal arguments, similar to court proceedings. Adjudication ensures decisions are made impartially, based on the evidence and the applicable law, providing a platform for justice within the administrative context.
Enforcement is how agencies ensure compliance with laws and regulations. The process includes investigations, sanctions, and corrective actions against entities or individuals who violate regulations. Enforcement actions are vital for upholding the integrity of legal and regulatory standards and protecting public interests, with administrative lawyers playing a key role in prosecuting and defending the actions.
Administrative law encompasses judicial review, a process where courts assess the legality of agency actions. Administrative law includes procedural rules outlined in the Administrative Procedure Act (APA), guiding agencies in rulemaking, adjudication, and other processes. The complex framework dictates agency organization and structure, requiring the expertise of an administrative lawyer to navigate the intricacies of how agencies are formed, agencies’ powers, and internal hierarchy.
The 3 types of administrative law form a comprehensive system that governs the conduct of administrative agencies and agencies’ interactions with the public. An administrative lawyer plays a crucial role in the ecosystem, helping individuals and organizations navigate the regulatory landscape more effectively.
Is Administrative Law On The Bar?
Yes, administrative law is on the Bar Exam in most jurisdictions within the United States, making it essential for aspiring administrative lawyers. Administrative law is extensively covered in both the Multistate Bar Exam (MBE) and the essay portions, reflecting its importance in law practice.
The MBE includes questions that test knowledge on various aspects of Administrative Law, such as judicial review standards, rulemaking procedures, due process requirements, and agency adjudication. The components are integral for administrative lawyers to understand how administrative agencies operate within the legal framework.
State Bar Exams feature essay questions specifically about administrative law. The tests candidates’ ability to apply legal principles to hypothetical scenarios, demonstrating their understanding of the complex area of law. The inclusion of administrative law in the Bar Exam underscores its crucial role, as understanding administrative processes and regulations is fundamental for legal practice.
Administrative lawyers intending to work closely with or within governmental agencies find the knowledge of administrative processes and regulations particularly vital.
Understanding administrative law is indispensable for passing the Bar Exam and for the practice of an administrative lawyer. It intertwines with other legal areas tested, such as Constitutional Law, Civil Procedure, and Torts, illustrating the pervasive nature of administrative regulations in various legal contexts. Mastery of administrative law not only aids in passing the Bar but prepares future lawyers for navigating the regulatory environment effectively.
What Is An Administrative Lawyer?
An administrative lawyer is a specialized legal professional who guides clients through government regulations and bureaucratic procedures. Administrative lawyers focus on ensuring legal compliance, representing clients in disputes with government entities, and advocating for clients’ rights in administrative matters. The expertise of an administrative lawyer is essential for navigating complex legal landscapes and securing favorable outcomes against governmental actions.
Administrative lawyers possess a deep understanding of legal frameworks governing agency operations. Administrative lawyers are pivotal in interpreting regulations, challenging administrative decisions, and ensuring fairness in government processes. Administrative lawyers’ work is crucial for maintaining the balance between governmental authority and individual rights, making them indispensable in the legal arena.
Administrative lawyers wear multiple hats; they serve as litigators, advisors, negotiators, and rulemaking advocates. Administrative lawyers represent clients in court against agency actions, provide counsel on navigating regulatory environments, negotiate settlements or modifications with agencies, and influence policy through rulemaking processes. The versatility allows administrative lawyers to protect clients’ interests effectively across various sectors, from individual rights to business operations.
Administrative lawyers play a crucial role in a world where governmental regulations touch nearly every aspect of life, ensuring the regulations are applied fairly and justly. Administrative lawyers hold agencies accountable, fight for transparency, and work towards more efficient and effective government interactions.
Administrative lawyers serve as more than mere legal representatives; they are guardians of the legal process, ensuring that government actions are conducted within the bounds of the law. Administrative lawyers offer a bridge between the complex world of administrative regulations and the individuals navigating administrative waters, providing clarity, protection, and a voice in seemingly impenetrable bureaucratic systems.
What Is The Importance Of An Administrative Lawyer?
The importance of an administrative lawyer lies in ensuring the legal system is balanced, protecting both individual and collective rights, enforcing government agency accountability, and enhancing efficiency within the complex domain of administrative law.
Administrative lawyers are indispensable as they guarantee due process by ensuring clients receive proper notification, have their voices heard, and contest unjust agency decisions. Standing against discriminatory practices and arbitrary actions from agencies safeguards individual and collective rights, ensuring fair treatment for all. Administrative lawyers are instrumental in providing access to justice through their expertise in navigating bureaucratic complexities.
Administrative lawyers hold government agencies accountable by monitoring their compliance with legal standards and procedures, thus preventing power misuse. Promoting transparency in decision-making processes, administrative lawyers encourage responsible governance. Administrative lawyers challenge unlawful or flawed decisions through judicial review, maintaining the rule of law.
Administrative lawyers streamline interactions between individuals, businesses, and government entities. Administrative lawyers assist in complying with regulations, obtaining permits, and resolving disputes efficiently. An administrative lawyer’s involvement in policy advocacy shapes fair and effective policies, representing clients’ interests in rulemaking processes.
Administrative lawyers’ importance spans various sectors, aiding individuals in benefits claims, immigration appeals, and protecting personal rights. Businesses benefit from administrative lawyers’ environmental, labor, and tax law compliance expertise. Non-profit organizations rely on administrative lawyers for policy advocacy and protecting clients affected by agency actions. Upholding the rule of law and ensuring checks and balances, administrative lawyers contribute significantly to a healthy democracy and a fairer society.
What Does An Administrative Lawyer Do?
An administrative lawyer skillfully navigates the complexities of administrative law, providing indispensable advice, advocacy, litigation, negotiation, and document drafting services to individuals interacting with government agencies.
Administrative lawyers serve as invaluable guides through the legal labyrinth, ensuring that clients comply with intricate regulations and helping them to foresee and mitigate potential legal issues. Crafting strategic plans facilitates smoother dealings with governmental entities and aims to secure the most advantageous outcomes while avoiding legal pitfalls.
Administrative lawyers serving as advocates are responsible for representing clients in hearings and presenting compelling arguments and evidence. Administrative lawyers adeptly negotiate settlements and craft documents that clearly articulate their clients’ positions, aiming to sway agency decisions in their favor. Administrative lawyers are prepared to enter the fray of litigation and challenge unjust agency actions in court through judicial review if negotiations fall short.
The responsibilities of administrative lawyers extend beyond the courtroom and negotiating table. Administrative lawyers actively participate in rulemaking, advocating for regulations that reflect their clients’ interests. Administrative lawyers conduct thorough investigations and due diligence to build a strong foundation for each case and educate clients and organizations on navigating the maze of legal compliance.
Specializing in diverse areas such as environmental law, healthcare, and immigration, administrative lawyers tailor their expertise to the specific needs of individuals, businesses, and non-profit organizations. An administrative lawyer’s effectiveness hinges on a deep understanding of legal principles, coupled with analytical skills, outstanding communication, negotiation prowess, and advocacy.
What Do Administrative Lawyers Do Daily?
Administrative lawyers, on a daily basis, meticulously navigate the complex intersection of law and government regulations, advocating for clients’ rights and ensuring compliance.
Administrative lawyer days often start with client consultations, discussing legal challenges, and strategizing the most effective paths forward. Administrative lawyers conduct extensive research to uncover relevant laws and precedents underpinning legal strategies. Administrative lawyers seamlessly weave the information into their advocacy. Drafting documents becomes crucial, requiring a careful balance of legal expertise and precision to articulate clients’ positions effectively.
Engaging with government agencies is a routine yet critical part of administrative lawyer days, involving negotiations, attending hearings, or presenting cogent arguments, all aimed at championing the clients’ interests. Administrative lawyers monitor regulatory developments, ensuring their actions always comply with the latest legal standards.
Administrative lawyers are prepared to step into the courtroom when litigation calls, armed with meticulously prepared pleadings and ready to argue persuasively before the judge. Administrative lawyers enrich professional growth and contribute to the legal community through networking, continuous learning, and pro bono engagements, extending involvement beyond the casework.
Administrative lawyers, in their daily endeavors, embody the principles of justice and fairness, skillfully guiding clients through the maze of administrative law. Administrative lawyer’s diverse activities spotlight their commitment to legal excellence and dedication to serving the public interest.
Do Administrative Lawyers Go To Court?
Yes, administrative lawyers go to court, although it’s not their primary setting. An administrative lawyer’s work mainly revolves around administrative hearings and procedures. Administrative lawyers appear in court to challenge agency decisions, seek judicial review of administrative rulings, appeal decisions, or enforce judgments. The dual capability demonstrates Administrative lawyers’ adeptness at navigating administrative and judicial landscapes to advocate for their client’s best interests.
Administrative lawyers, while operating within the specialized realm of administrative hearings, possess the expertise to transition into the judicial court system when necessary. An administrative lawyer’s strategic approach to each case ensures that clients receive comprehensive legal representation, safeguarding their rights across all forums. The versatility underscores Administrative lawyers’ crucial role in the broader legal ecosystem, adeptly bridging the gap between administrative tribunals and courts.
Do Administrative Lawyers Handle Constitutional Law?
No, administrative lawyers do not handle constitutional law cases directly. Administrative law focuses on regulating the actions of government agencies, involving specific regulations and procedures. Constitutional law involves a broader spectrum of legal issues, dealing with the interpretation and application of the Constitution, in contrast to other legal fields.
The core focus of administrative lawyers on agency regulations and compliance contrasts with the requirement in constitutional law for a distinct understanding of constitutional rights and principles. Administrative lawyers consult with experts in constitutional law, including constitutional lawyers, to ensure a comprehensive legal approach when agency actions are challenged on constitutional grounds. The primary expertise of administrative lawyers firmly resides in the realm of administrative law, emphasizing agency-specific legal frameworks, even as intersections and overlaps with constitutional law occur.
Administrative lawyers primarily navigate the intricate legal landscape of government agency regulations, even though there are occasional intersections between administrative and constitutional law. An administrative lawyer’s expertise is crucial for understanding and managing the specific legal challenges within the domain. Collaboration with constitutional lawyers ensures the most effective representation of constitutional matters, highlighting the specialized nature of legal practice in distinct but occasionally intersecting fields.
How Long Does It Take To Become An Administrative Lawyer?
To become an administrative lawyer takes at least 7 years of post-secondary education. The duration includes 4 years to earn a bachelor’s degree and 3 additional years to complete law school and obtain a Juris doctorate. Passing the bar exam, which varies by state but generally involves months of preparation and testing, is essential after law school. Becoming an administrative lawyer starts with a solid 7-year educational foundation, thus marking the beginning of the journey.
Administrative lawyers pursue further specialization through LLM or Master’s degrees in fields like Public Administration or Environmental Law, adding 1 to 2 years to their educational timeline. Advanced degrees deepen an administrative lawyer’s expertise in the chosen area, making administrative lawyers more competitive in the job market. Completing a clerkship, which typically lasts 1 year, offers practical experience and insights into the judicial process, further extending the timeline.
Securing the right job extends the timeline beyond the initial 7 years. Finding a position that aligns with an administrative lawyer’s specialization and career goals is time-consuming, depending on the job market and the lawyer’s interests. Specializing in a niche area of administrative law necessitates additional training or certifications, potentially adding more time before one practices as an administrative lawyer.
Factors such as academic performance, work experience, networking, and location influence the time it takes to become an administrative lawyer. Stellar academic records and relevant work experience expedite securing a desirable position, while strong professional networks provide otherwise inaccessible opportunities. The competitiveness of the legal market in certain areas affects how quickly an administrative lawyer finds a position that suits their specialization and career aspirations.
The base timeline to become an administrative lawyer is about 7 years, and several factors extend the period, like advanced degrees, clerkships, job market conditions, and specialization requirements, which are significant considerations. Administrative lawyer’s journey is unique, influenced by their educational choices, experiences, and professional networks.
What Is The Best Major To Become An Administrative Lawyer?
The best major to become an administrative lawyer is undoubtedly Law, focusing on administrative or public law. The specialized area prepares students for the specific challenges and complexities of working within government regulation and administrative proceedings. Studying law allows aspiring administrative lawyers to deeply understand the legal principles governing public administration and government policy enforcement.
A major in Political Science stands out as a strong foundation for a career as an administrative lawyer. The discipline offers comprehensive insights into government structures, policies, and the legal framework governing public administration. Political Science majors are well-prepared to understand the complexities of administrative law, making it an excellent choice for individuals pursuing an administrative lawyer career path.
Public Administration is another pivotal major for aspiring administrative lawyers. Public Administration focuses on the management of public agencies and offers a clear understanding of regulatory management and policy analysis. Students interested in the administrative processes and legal challenges faced by government agencies find that public administration provides critical insights essential for a career in administrative law.
A major in Public Policy is invaluable for individuals looking to specialize in the policy aspects of administrative law. The major sharpens skills in policy development, analysis, and evaluation, preparing students for the regulatory and policy-oriented challenges they face as administrative lawyers. It’s an ideal choice for individuals focused on impacting policy and regulatory practices.
The Economics major is particularly beneficial for administrative lawyers. The analytical thinking and understanding of market dynamics it fosters are crucial for individuals dealing with the economic implications of legal and regulatory decisions. Economic analysis provides a strong foundation for administrative lawyers involved in competition law or sectors where economic analysis is key.
A major in Environmental Studies is essential for individuals aiming to become administrative lawyers within the environmental sector. The field offers a grounding in environmental policy, law, and regulations, equipping students to tackle legal challenges related to environmental protection. The major is perfectly suited for individuals dedicated to navigating the intricacies of environmental law and regulation.
Choosing the right major is pivotal for anyone aspiring to become an administrative lawyer. Focused study in law, governmental insights in Political Science, the administrative depth of Public Administration, or other relevant fields offer unique benefits. The benefits from the areas are tailored to the multifaceted nature of administrative law, providing specific focus areas or a broad understanding, whether through individual merits or collective value.
What Are The Best Law Schools For Administrative Law?

The 10 best law schools for administrative law are listed below.
- Georgetown University Law Center: Situated in the heart of the nation’s capital, Georgetown University Law Center is a prime choice for students aspiring to become administrative lawyers. The law school comprehensive program includes over 30 specialized courses, offering depth in environmental law and healthcare law. Georgetown’s proximity to federal agencies provides unique internships and networking opportunities, enhancing students’ practical experience.
- New York University School of Law: NYU Law stands out for its broad curriculum and renowned faculty, including leaders in environmental law and regulation. The Engel Center on Innovation & Regulation exemplifies the school’s commitment to studying and shaping contemporary regulatory policies. The law school offers students a dynamic environment to explore the nuances of Administrative law and prepare for careers as administrative lawyers.
- University of California, Berkeley School of Law: Berkeley Law takes a critical and interdisciplinary stance, incorporating perspectives from law, economics, and political science. The law school specialized clinics, such as the Environmental Law Clinic, provide practical training that complements classroom learning, preparing students to become adept administrative lawyers equipped to tackle complex legal issues effectively.
- University of Chicago Law School: Emphasizing an interdisciplinary approach, the University of Chicago Law School integrates economic, political science, and legal insights into its administrative law curriculum. The law school crafts administrative lawyers with a profound understanding of the field’s complexities. Its Center for the Study of Constitutional Rights and Law School Policy Lab fosters a deep engagement with regulatory policies, offering students avenues for research and advocacy.
- Northwestern University Pritzker School of Law: Northwestern Law’s Center for Public Law and Policy is a hub for scholarship and practical activities in administrative law. The curriculum covers various topics, including environmental and healthcare law, supported by specialized clinics that offer real-world experience in navigating legal and regulatory challenges. The law school’s comprehensive approach molds students into skilled administrative lawyers adept at handling complex regulatory issues.
- Columbia Law School: Columbia Law School’s program, rich in diversity, covers environmental, healthcare, and telecommunications law, equipping students to become adept administrative lawyers. The law school practical learning components, like workshops, seminars, and clinics, enable the application of knowledge in real-world settings, fostering a deep understanding of legal frameworks governing administrative actions.
- Duke University School of Law: Duke Law, blending insights from economics, political science, and legal studies, prepares students to excel as administrative lawyers. The law school’s specialized courses and clinics in energy and healthcare law address the complexities of administrative law practice, emphasizing a deep understanding of regulatory processes and legal theory.
- Yale Law School: Yale Law offers an exceptional program focusing on administrative law and constitutional theory. The curriculum includes various topics, providing opportunities for specialized legal writing and seminars. Yale’s renowned faculty and commitment to legal scholarship make it a leading institution for aspiring administrative lawyers.
- UCLA School of Law: UCLA Law’s Center for Law & Economics offers an interdisciplinary view on regulatory issues, enriching students’ understanding of administrative law.UCLA Law’s curriculum, offering courses and clinics in environmental, healthcare, and antitrust law, equips students to become skilled administrative lawyers. The hands-on experience prepares students for the intricate legal challenges of regulation and policy-making.
- University of South Carolina School of Law: The University of South Carolina distinguishes in legal education by preparing students for successful careers as administrative lawyers. An innovative Externship Program enables the students to work directly with federal or state agencies, placing the university among the top law schools in South Carolina. The hands-on experience, including drafting legal documents and observing legal proceedings, arms students with the necessary skills to navigate the complexities of governmental and regulatory environments efficiently.
When Are Administrative Lawyers Needed?
Administrative lawyers are needed when individuals, businesses, or organizations interact with government regulations or agencies. Administrative lawyers specialize in navigating the complex landscape of administrative law, offering indispensable support in various contexts.
An administrative lawyer becomes a critical ally when challenging agency decisions, such as a license denial or a regulatory compliance issue. A 2021 study by the American Bar Association (ABA) highlights the workload of administrative lawyers. The study found that 75% of administrative lawyers spend between 26-75% of their time on litigation and advocacy before government entities.
Handling complex regulations is another scenario where the expertise of an administrative lawyer is invaluable. Government regulations are becoming increasingly intricate across different industries, and administrative lawyers guide clients through the regulatory maze, ensuring compliance and protecting them from potential legal pitfalls. The guidance is crucial for businesses navigating licensing, permitting, and regulatory compliance issues.
Administrative lawyers play a pivotal role in business and corporate matters. A 2023 ABA survey highlighted that most administrative lawyers deal with licensing and permitting, helping businesses secure the necessary approvals to operate legally. Administrative lawyers represent clients in disputes with licensing agencies, safeguarding their ability to conduct business.
Individual rights and benefits cases, such as social security, disability benefits, and immigration issues, necessitate the expertise of administrative lawyers. Administrative lawyers assist clients in navigating application processes, appeals, and hearings, advocating for their rights and benefits in the face of complex bureaucratic procedures.
Environmental and public interest advocacy further exemplifies the need for administrative lawyers. The legal experts represent groups or individuals in challenging environmentally harmful practices or government decisions, advocating for policy changes that promote the public interest and protect the environment.
Administrative lawyers ensure fair and legal outcomes for individuals and businesses alike. Administrative lawyers bridge the gap between complex government regulations and the entities required to follow them, playing a crucial role in various legal and regulatory issues.
How Do Administrative Lawyers Handle Complex Regulations?
Administrative lawyers handle complex regulations by effectively dissecting them to guide their clients through legal challenges. Administrative lawyers begin by thoroughly analyzing laws and statutes, laying a solid foundation for understanding the nuances that impact their clients’ cases. The detailed approach ensures a well-informed strategy for navigating the regulatory maze.
Administrative lawyers guide individuals and organizations through regulatory frameworks with deep legal knowledge, strategic thinking, and practical experience, minimizing risks and leveraging legal avenues for advantageous outcomes.
Administrative lawyers engage in comparative analysis to uncover different interpretations of regulations, serving as a further step in their comprehensive approach. The method allows administrative lawyers to anticipate potential challenges and identify opportunities, showcasing their deep understanding of the legal landscape. The expertise of administrative lawyers in regulatory law becomes evident as they navigate through the varied interpretations with ease.
Administrative lawyers have a deep knowledge of administrative procedures, which is essential for guiding clients through regulatory processes, which serves as an additional advantage. Mastering the procedures prepares clients for hearings, appeals, and any procedural obstacles, highlighting the importance of their role in the regulatory field.
Administrative lawyers, in their evidence-gathering role, meticulously collect and analyze data to build strong cases. The preparation underscores administrative lawyers’ dedication to client success, demonstrating their commitment to thorough legal advocacy. The strategic use of evidence is key to their effectiveness in regulatory disputes.
Utilizing the Freedom of Information Act, an administrative lawyer accesses vital agency documents, gaining insights into regulatory decision-making. The access provides a strategic advantage, enhancing administrative lawyers’ ability to navigate complex regulatory environments. The insights prove invaluable in advocating for their clients’ interests.
Administrative lawyers constantly adapt to regulatory changes, ensuring their clients remain compliant and informed. The proactive approach of administrative lawyers to legal developments is crucial for managing the dynamic nature of regulatory law. The adaptability of administrative lawyers is a testament to their commitment to protecting their client’s interests in an evolving legal landscape.
Administrative lawyers are essential navigators in the complex world of regulations, combining legal expertise with strategic planning and effective advocacy. Administrative lawyers ensure that individuals and businesses comply with current laws and are well-positioned to adapt to future changes.
How Do Administrative Lawyers Make Sure Rules Are Followed?
Administrative lawyers make sure rules are followed by serving as pivotal guardians of legal compliance, ensuring government actions align with laws. Administrative lawyers meticulously analyze regulations, advising clients on navigating the intricate legal landscape.
Administrative lawyers challenge arbitrary decisions through strategic litigation and advocacy, safeguarding individual and business interests. The expertise of administrative lawyers in administrative law prevents unlawful government actions, protecting the public from potential injustices.
Administrative lawyers hold government agencies accountable by challenging actions that exceed their legal authority or misinterpret regulations. Administrative lawyers scrutinize agency decisions through judicial reviews and administrative challenges, ensuring they are made transparently and based on sound legal principles. The vigilance helps balance government powers and individual rights, fostering a transparent environment where decisions are made in the public’s interest.
Administrative lawyers ensure fair treatment for all under the law to protect individual rights. Administrative lawyers defend against the overreach of governmental power, advocating for due process and the right to a fair hearing. Negotiating settlements or representing clients in administrative hearings, administrative lawyers ensure that the voices of individuals and businesses are heard, safeguarding them from unjust or biased decisions.
Administrative lawyers influence the broader regulatory landscape beyond individual cases, serving as an additional benefit to their role. Administrative lawyers engage in policy advocacy, contribute to legislative reform, and participate in public education efforts to demystify complex regulations for the general public. Administrative lawyers help shape a fairer, more equitable legal framework that respects both the letter and the spirit of the law, ensuring that regulations are applied justly and consistently through the actions, serving additionally as a foundational element of their practice.
Administrative lawyers are the linchpins in ensuring that government agencies operate within the confines of the law, protecting individual rights, and shaping a just regulatory environment. The expert navigation of the legal system ensures that rules are followed and applied fairly and equitably.
How Much Is The Salary Of Administrative Lawyers?
The average annual salary for an administrative lawyer in the United States, as of February 15, 2024, is $100,626. The figure corresponds to an hourly rate of approximately $48.38, or $1,935 weekly, and $8,385 monthly, showcasing a substantial earning potential within the legal specialty.
The salary of an administrative lawyer varies significantly based on 4 key factors: experience, geographic location, the type of employer, and specialization within administrative law. Experience levels are crucial, with seasoned professionals commanding higher salaries than their entry-level counterparts. Geographic location impacts earnings, as lawyers in metropolitan areas with a higher cost of living, such as San Jose, California, often receive salaries that exceed the national average by up to 97%. The type of employer is another determinant, with private law firms generally offering more competitive salaries than government agencies or non-profit organizations. Specialization within administrative law influences earning potential, as niche areas of high-demand practice offer higher compensation.
Other considerations such as education and qualifications, performance and reputation, and the benefits package employers offer significantly affect the overall compensation of administrative lawyers and the salary factors. Administrative lawyer salary prospects are often brighter for individuals who have graduated from prestigious law schools or possess additional certifications, as they access better opportunities and higher salaries. Performance-based bonuses and benefits like health insurance and retirement plans contribute to the compensation package.
Are Administrative Lawyers The Highest-Paid Lawyers?
No, administrative lawyers are not the highest-paid lawyers. The average annual salary for an administrative lawyer in the United States is approximately $100,626. The figure positions administrative law as a well-compensated field within the legal profession, yet not at the pinnacle of lawyer salaries.
The legal specialties often command higher average earnings than administrative lawyers; for instance, patent and intellectual property law specialists earn more than $180,000, reflecting the high demand for their expertise, a comparison that highlights the variance in compensation across legal fields.
Administrative lawyers earn well, but corporate and medical lawyers, with top earners making over $500,000, show higher earning potential based on their practice and clients.
The salary of an administrative lawyer, though respectable, is shaped by variables including geographic location, years of experience, and the employment sector, ranging from private practice and government agencies to in-house positions within corporations. Specialization within administrative law impacts earning potential, with lawyers focusing on high-demand areas, possibly commanding higher salaries.
Administrative lawyers earn respectable salaries, but they do not top the list of highest-paid legal professionals. Administrative lawyers’ compensation, while competitive, falls short of the earnings in other legal specialties, which are boosted by higher market demands, the complexity of the subject matter, and the significant financial stakes involved in the legal issues they tackle.
What Are The Benefits Of Administrative Lawyers?
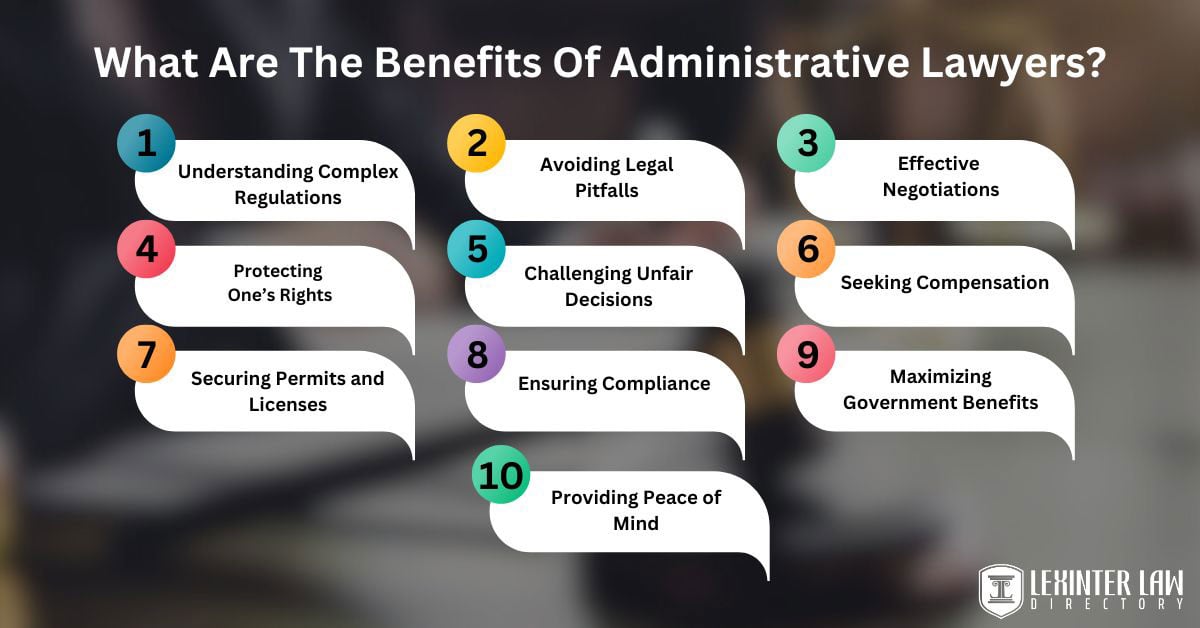
The 10 key benefits of administrative lawyers are listed below.
- Understanding Complex Regulations: Administrative lawyers have extensive knowledge of intricate legal frameworks and procedures. The expertise is invaluable for clients needing to navigate the maze of government regulations, saving them time and ensuring their endeavors are built on a solid legal foundation.
- Avoiding Legal Pitfalls: Foreseeing potential legal issues, administrative lawyers guide their clients away from costly mistakes and legal violations. An administrative lawyer’s proactive approach to identifying and addressing potential legal challenges before they escalate prevents significant financial and reputational damage.
- Effective Negotiations: Administrative lawyers leverage their specialized knowledge to negotiate effectively with government entities. The ability of administrative lawyers to communicate and advocate on behalf of the clients ensures that negotiations are conducted efficiently, often leading to favorable outcomes that align with their client’s goals and interests.
- Protecting One’s Rights: Administrative lawyers protect clients’ rights during administrative proceedings. Administrative lawyers defend their client’s legal rights, advocating for fair treatment or challenging unlawful actions.
- Challenging Unfair Decisions: Clients face adverse decisions by government agencies, and administrative lawyers stand ready to challenge the actions. Their expertise in administrative law enables them to contest decisions that are unlawful or violate clients’ rights, striving for justice and corrective measures.
- Seeking Compensation: Administrative lawyers pursue financial compensation when government actions have wronged clients. Administrative lawyer’s skillful navigation of legal processes leads to the recovery of damages, providing financial relief and justice for their clients.
- Securing Permits and Licenses: Administrative lawyers play a crucial role in applying for permits, licenses, and other government approvals. The guidance of administrative lawyers ensures that applications are correctly filed and processed, reducing delays and increasing the chances of approval.
- Ensuring Compliance: Administrative lawyers help clients ensure their operations fully comply with relevant regulations. The preventative measure avoids penalties and fortifies the client’s reputation and operational integrity.
- Maximizing Government Benefits: Administrative lawyers advise clients on how to apply for and maximize benefits from government programs. Their insight uncovers opportunities and strategies clients lack, leading to significant advantages.
- Providing Peace of Mind: Knowing that a knowledgeable and experienced administrative lawyer manages legal affairs offers clients peace of mind. The confidence allows clients to focus on their core activities and ensure that legal matters are in competent hands.
Can Administrative Lawyers Become Judges?
Yes, administrative lawyers can become judges, though the pathway involves certain considerations and varies by jurisdiction. States across the U.S. generally mandate that candidates for judicial positions possess substantial experience as practicing attorneys, frequently within courtroom environments. Administrative lawyers typically work within specific regulatory frameworks and do not engage in traditional courtroom litigation. Administrative lawyer’s expertise in administrative law and procedural intricacies serve as a valuable foundation for judicial roles.
Jurisdictions in some areas ease the transition from administrative lawyer to judge by recognizing the significance of experience in administrative hearings and decision-making through specific exceptions. Administrative law judges (ALJs), who preside over hearings and render decisions within government agencies, demonstrate skills in adjudication and legal analysis comparable to the skills used in courtrooms. ALJs boasting extensive experience and a profound grasp of legal principles often encounter opportunities to transition into judicial positions, especially within specialized courts pertaining to tax, environmental law, or other regulatory domains.
The route to becoming a judge often involves political appointments as well. Administrative lawyers with significant professional accomplishments and strong networks within the legal community or political sphere are appointed to judgeships in certain cases. The pathway, however, is more common at the state or local level, where the appointment process sometimes accommodates a wider range of legal backgrounds, including lawyers specialized in administrative law.
The transition from an administrative lawyer to a federal judge is notably more challenging due to the stringent requirements for federal judicial positions, which typically demand extensive litigation experience and a notable presence in the legal field. Administrative lawyers with exceptional qualifications, such as significant adjudicative experience as ALJs and a robust legal scholarship or public service record, are considered for prestigious roles, albeit infrequently.
Obstacles exist, particularly for federal judgeships, yet administrative lawyers with the right mix of experience, strategic career planning, and professional networking have viable pathways to becoming judges.
What Are The Downsides Of Administrative Lawyers?
The 10 downsides of administrative lawyers are given below.
- High Hourly Rates: Administrative lawyers command high hourly fees due to their specialized expertise, which significantly increases the cost of legal representation, especially in complex cases. The financial aspect requires careful consideration when hiring an administrative lawyer to navigate regulatory landscapes.
- Retainer Fees: Engaging an administrative lawyer often involves paying a retainer fee upfront, adding to the financial burden. The requirement underscores the importance of budget planning before seeking specialized legal services in administrative matters.
- Limited Pro Bono Work: Compared to other legal areas, administrative lawyers are less inclined to offer pro bono services because of the specialized nature of their work. The limitation restricts access to expert legal guidance in administrative law for the ones unable to afford it.
- Lengthy Legal Processes: Dealing with administrative law cases through an administrative lawyer is time-consuming owing to the complexity and length of legal procedures. The extended timeframe necessitates patience and long-term commitment from clients seeking to navigate bureaucratic systems.
- Limited Availability: The high demand for experienced administrative lawyers leads to limited availability, making securing prompt appointments or responses challenging. The factor is crucial when timely legal advice or action is required in administrative matters.
- Potential Delays: Administrative lawyers face delays due to unforeseen circumstances or backlogs in government agencies, extending the duration of legal processes. The delays highlight the unpredictable nature of dealing with administrative law and the need for flexibility.
- Revolving Door Concerns: Administrative lawyers have backgrounds in government agencies, raising questions about their ability to represent clients impartially against former employers. The potential conflict of interest warrants careful consideration when selecting a lawyer.
- Multiple Client Conflicts: Administrative lawyers representing multiple clients encounter conflicts of interest, necessitating transparent disclosure and ethical management to maintain trust and effectiveness in legal representation.
- Specialization Limitations: The specialization of administrative lawyers in specific legal issues varies, impacting the effectiveness of the lawyer’s representation. Specialization limitations underscore the importance of seeking a lawyer with relevant expertise in administrative law.
- Personality and Communication Fit: The success of legal representation often depends on a good personality and communication fit between the client and the administrative lawyer. Ensuring compatibility is crucial for a productive attorney-client relationship in navigating administrative legal challenges.
What Are The Skills Required As Administrative Lawyers?

The 12 skills required as administrative lawyers are listed below.
- In-depth Knowledge of Administrative Law: Administrative lawyers must possess an exhaustive understanding of statutes, regulations, case law, and the procedures of various agencies. The comprehensive knowledge base is critical for interpreting laws accurately, advising clients effectively, and ensuring legal strategies are built on solid legal grounds.
- Research and Analysis: Administrative lawyers excel in conducting detailed legal research and analyzing complex legal issues. Administrative lawyers meticulously examine legal precedents, statutes, and regulatory materials to uncover relevant information, enabling them to construct well-founded arguments and strategies for their clients.
- Strong Writing and Communication Skills: The ability to articulate legal arguments clearly and persuasively in writing is paramount. Administrative lawyers draft various legal documents, including briefs, motions, and pleadings, requiring exceptional writing skills to effectively influence decisions and advocate for clients’ interests.
- Procedural Mastery: A deep understanding of the procedural nuances of administrative hearings and agency processes is essential. Administrative lawyers navigate the procedures with expertise, ensuring that cases are presented effectively and that all procedural requirements are meticulously followed.
- Navigating Bureaucratic Systems: Dealing with government agencies and navigating their complex bureaucratic systems is a hallmark of administrative law. Administrative lawyers adeptly manage the interactions, understand agency protocols, and ensure timely compliance with all regulatory requirements.
- Alternative Dispute Resolution: Proficiency in mediation and negotiation allows administrative lawyers to resolve disputes without litigation, saving clients time and resources. Alternative dispute resolution skills are crucial for facilitating agreements and achieving settlements favorable to their clients.
- Advocacy and Negotiation: Effective advocacy and negotiation skills are central to an administrative lawyer’s role. Administrative lawyers adeptly present cases before administrative judges and officials, negotiating settlements and advocating for clients’ rights with persuasive oral and written arguments.
- Building Relationships: The ability to forge strong relationships with agency officials, opposing counsel, and judges significantly influence case outcomes. Administrative lawyers use interpersonal skills to navigate the legal system effectively, benefiting the clients’ cases.
- Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills: Administrative lawyers are skilled problem solvers, capable of analyzing intricate legal issues and identifying innovative solutions. Administrative lawyers’ analytical prowess supports strategic decision-making, ensuring that they navigate complex regulatory landscapes successfully.
- Attention to Detail: The complex nature of administrative law demands acute attention to detail. Administrative lawyers scrutinize regulations and legal documents, ensuring accuracy and compliance and safeguarding against potentially costly errors.
- Client Communication and Management: Maintaining open, effective communication with clients is crucial. Administrative lawyers keep clients informed, manage their expectations, and build trust through clear, consistent communication, ensuring that clients are fully aware of their case’s progress and prospects.
- Research and Technology Skills: Proficiency in legal research tools and technology enhances an administrative lawyer’s efficiency. Administrative lawyers leverage technology to streamline research, manage case information, and maintain up-to-date knowledge of regulatory changes, optimizing their practice and client service.
How Important Are Communication Skills For Administrative Lawyers?
Communication skills are critically important for administrative lawyers. Administrative lawyers depend on their ability to clearly articulate complex legal principles and administrative procedures to audiences, such as clients, judges, and government officials. An administrative lawyer must distill intricate regulations and legal jargon into understandable language, ensuring clients fully grasp their rights and options. The clarity aids in building trust and confidence between the lawyer and their clients, laying the foundation for effective legal representation.
An administrative lawyer’s ability to negotiate and advocate is largely predicated on their communication prowess. The capacity of a lawyer to present arguments coherently and compellingly plays a crucial role in the outcome of their cases. Drafting persuasive legal briefs, arguing before an administrative tribunal, or negotiating with regulatory agencies are key activities where such skills are essential. Effective communication facilitates smoother negotiations and enhances the lawyer’s ability to advocate for their client’s interests, making it a critical skill in administrative law.
The role of an administrative lawyer often involves navigating complex bureaucratic landscapes, where clear and effective communication is essential for successfully liaising with government agencies and officials. The skill set enables lawyers to expedite processes, avoid misunderstandings, and achieve favorable resolutions on behalf of their clients. An administrative lawyer’s success relies heavily on communication skills, emphasizing the skill’s critical importance in their professional toolkit.
An administrative lawyer’s communication skills are not merely an asset but an essential component of their professional toolkit, integral to achieving success and advancing the interests of their clients within the intricate framework of administrative law.
How Do Administrative Lawyers Differ From Other Lawyers?
Administrative lawyers differ from other lawyers primarily in their specialized focus on navigating regulations, statutes, and procedures related to government agencies.
Administrative lawyers possess a deep understanding of specific regulatory areas such as environmental law, healthcare, or telecommunications, unlike lawyers in other areas who deal with broader legal principles. The specialization enables them to effectively advocate for their clients in complex regulatory environments.
Administrative lawyers distinguish themselves further by possessing unique expertise in understanding government agencies’ internal workings and decision-making processes. Administrative lawyers’ expertise allows them to anticipate challenges, strategize effectively, and navigate the bureaucratic systems often present within the agencies. Administrative lawyers often spend less time in traditional courtrooms and more in administrative proceedings, emphasizing proficiency in the specific rules of evidence, the burden of proof, and procedures governing the environment.
Administrative lawyers are adept at utilizing alternative dispute resolution methods to efficiently resolve conflicts, a skill that sets administrative lawyers apart from their counterparts in more litigation-focused legal fields. Administrative lawyers tailor advocacy, adapt it to specific agencies and decision-making bodies, and showcase the nuanced approach to legal persuasion within the administrative context. The specialized form of advocacy is crucial for representing individuals, businesses, or organizations before administrative agencies, protecting their rights and interests in various regulatory contexts.
Administrative lawyers play a pivotal role in the legal landscape through specialized knowledge and skill sets, distinguishing them significantly from lawyers in other practice areas.
What Is The Difference Between Administrative And Constitutional Lawyers?
The difference between administrative and constitutional lawyers lies in their areas of specialization; administrative lawyers specialize in the rules and regulations of government agencies, while constitutional lawyers focus on issues related to the interpretation and implementation of the Constitution.
Administrative lawyers are the navigators of the legal world when it comes to dealing with government regulations and administrative agencies. Administrative lawyers specialize in understanding and applying the laws that govern administrative procedures, focusing on areas such as environmental law, healthcare, and employment. Administrative lawyers often represent clients in administrative hearings and work to ensure that government actions comply with established regulations.
Constitutional lawyers deal with issues that challenge or seek to interpret the Constitution, operating on a broader legal canvas. The work of a Constitutional lawyer is fundamental to protecting the rights and freedoms guaranteed by the Constitution, addressing issues like freedom of speech, the right to privacy, and equal protection under the law. Administrative lawyers focus on regulatory compliance and administrative hearings, while constitutional lawyers represent clients in high-stakes cases that have the potential to set significant legal precedents, often arguing before state and federal courts, including the Supreme Court.
The key difference between administrative and constitutional lawyers lies in the scope of their practice. Administrative lawyers are experts in administrative law’s specific, often technical, rules and procedures. Administrative lawyers work within government agencies and are adept at navigating the complex bureaucracies that regulate various aspects of public and private life. Constitutional lawyers, by contrast, engage with the foundational principles of law and governance, challenging and defending the interpretation of the Constitution in various contexts. Constitutional lawyer’s work directly impacts the legal standards that govern society.

