Sports Law: Understanding Regulations And Legal Issues In Sports
Sports law is a specialized area of law that addresses legal issues and disputes within the sports industry. Sports law plays a pivotal role in shaping the framework within which athletes, teams, and sporting organizations operate by focusing on the intersection of various legal practices with sports-related matters. The law encompasses everything from contract negotiations and employment law for athletes and staff to regulating sports agencies and associations. Sports law governs professional and amateur sports, ensuring all participants adhere to international standards and regulations.
There are 5 main types of sports law. First, contract law in sports deals with agreements between athletes, clubs, and sponsors, specifying rights, responsibilities, and financial details. Second, intellectual property law in sport protects trademarks, logos, and broadcasting rights, which are crucial for brand protection and revenue generation. Third, sports law covers personal injury cases, providing a pathway for athletes to claim compensation for competition or training injuries. Fourth, sports law incorporates anti-doping regulations, maintaining competition integrity and fairness. Sports law includes arbitration and litigation processes as the fifth key component, offering legal avenues for dispute resolution within the sports industry.
The principle of sports law emphasizes fairness, integrity, and the promotion of equal opportunities within the sports industry. The law ensures that athletes and organizations adhere to established rules, fostering a competitive environment that values sportsmanship. Sports law seeks to protect the legal rights of all stakeholders, from players to governing bodies, ensuring disputes are resolved fairly and equitably.
Sports law regulation establishes a comprehensive set of guidelines for the sports industry, ensuring fair play and integrity. The regulations encompass contract management, doping control, athlete safety, and intellectual property rights, addressing the multifaceted nature of sports. Implementing clear standards of sports law regulation fosters transparency and accountability among athletes, teams, and organizations. The law safeguards the competitive spirit of sports while protecting all stakeholders’ legal and commercial interests. The framework is crucial for maintaining the ethical and operational standards of the sports world.
Legal issues in sports law range from doping and contract disputes to intellectual property and personal injury claims. The challenges necessitate specialized legal expertise to ensure fairness and compliance within the sports industry. Sports law plays a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of sports competitions and the welfare of athletes addressing issues. The law highlights the demand for professionals in sports law jobs who navigate complex matters.
The importance of sports law extends beyond resolving disputes; the law underpins the sports industry’s ethical, commercial, and operational framework. The legal field ensures the rights of athletes, teams, and stakeholders are protected while promoting fair play and competition. Sports law facilitates the growth of sports law jobs, offering career opportunities for individuals dedicated to upholding justice and integrity in sports. The law contributes significantly to the sustainable development and reputation of sports globally by establishing clear regulations and guidelines.
Sports lawyers play a crucial role in navigating the complex legal landscape of the sports industry. The professionals ensure compliance with sports law, safeguarding the interests of athletes, teams, and organizations. Resolving disputes and negotiating contracts, sports lawyers contribute significantly to the integrity and fairness of sports. The expertise of a sports lawyer is indispensable for maintaining the legal health of the sports world.
Table of Contents
- What Is Sports Law?
- What Are The Principles Of Governing Sports Law?
- What Is The Role Of Contract Law In Professional Sports?
- What Legal Considerations Are Relevant For Sports Sponsorship And Endorsements?
- How Are Broadcasting Rights Regulated Within Sports Law?
- What Is The Importance Of Health And Safety Regulations In Sports Law?
- How Do Transfer Regulations Impact Players And Teams In Professional Sports?
- What Are The Ethical Considerations And Challenges In Sports Law?
- How Are Immigration And Visa Issues Handled For International Athletes?
- How Does Sports Law Address The Use Of Performance-Enhancing Substances?
- How Is Governance Structured In Sports Organisations, And What Legal Issues Arise?
- How Does Child Protection And Welfare Integrate Into Sports Law Policies?
- How Does Sports Law Regulate Fan Interactions And Behaviours?
- How Does Sports Law Treat Issues Of Privacy And Publicity In The Athletic Community?
- What Is A Sports Law Degree?
What Is Sports Law?
Sports law is a distinct branch of law that governs the sports industry, covering a wide array of legal areas. The legal field addresses issues involving athletes, teams, leagues, sports organizations, and their relationships. Sports law encompasses contract law, tort law, antitrust law, labor law, and intellectual property law, applying the principles to the unique context of sports to ensure fairness, safety, and integrity.
Sports law is crucial in addressing disputes, managing contracts, and protecting rights within the sports domain. Sports law plays a vital part in regulating the conduct of players, teams, and governing bodies, ensuring competitive balance and the equitable treatment of all parties involved. The legal field tackles doping-related issues, broadcasting rights, and fan safety, highlighting the comprehensive scope.
Sports law facilitates conflict resolution, agreement negotiation, and rule enforcement, providing a structured environment for all stakeholders. The sports industry operates within a legal framework that promotes integrity, fairness, and the overall growth of sports through sports law.
Sports law was not implemented at a specific date but evolved with the professionalization of sports in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The evolution was driven by the need to manage the complexities of sports as a business. The growth of the sports industry necessitated the development of sports law to address contracts, injuries, and regulations.
The development of sports law paralleled the increasing commercialization and internationalization of sports. The law in sport became essential for resolving disputes, ensuring fair play, and protecting athletes’ and organizations’ rights. The legal framework has become integral to the sports industry, addressing various issues from contracts to doping.
The emergence of sports law reflects the growing recognition of sports as a significant sector requiring specialized legal expertise. Sports law provides the necessary legal infrastructure to support the integrity, fairness, and smooth operation of sports worldwide. Sports law continues to evolve, responding to new challenges and opportunities in the sports industry.
What Are The Principles Of Governing Sports Law?

The 10 principles of governing sports law are listed below.
- Fair Play and Level Playing Field: Fair play and a level playing field within sports law aim to create an equitable environment for all athletes and teams. The principle addresses issues like doping and match-fixing, ensuring regulations regarding equipment and gameplay are uniformly applied and promoting fairness in competition.
- Contractual Integrity: The principle of Contractual Integrity in sports law mandates that all agreements, including player contracts, endorsement deals, and broadcasting rights, are conducted fairly and transparently. Contractual integrity emphasizes the importance of honoring commitments to protect the interests of all parties involved in sports.
- Due Process and Natural Justice: Due process and natural justice are fundamental in sports law, ensuring fair treatment in disciplinary actions and disputes. The principle guarantees that all proceedings, from hearings to drug testing, are conducted impartially, providing a fair avenue for review and appeal.
- Antitrust and Fair Competition: Antitrust and fair competition are crucial principles in sports law, designed to prevent monopolies and ensure a healthy competitive environment. They safeguard against restrictions on player movements and balance players’ rights with the broader interests of the sport.
- Dispute Resolution: Dispute resolution in sports law promotes efficient and effective conflict resolution mechanisms. Dispute resolution advocates for alternative dispute resolution methods including arbitration and mediation, to quickly settle disputes and avoid lengthy legal battles.
- Protecting Athlete Welfare: The principle of protecting athlete welfare in sports law prioritizes the health and safety of athletes. The principle focuses on implementing safety measures, rules against dangerous play, and ensuring fair compensation for athletes who suffer career-ending injuries.
- Promoting Sportsmanship and Ethics: Promoting sportsmanship and ethics is a key principle of sports law, emphasizing the importance of ethical conduct and good sportsmanship. The principle discourages misconduct and fosters respect among competitors and officials, maintaining ethical practices within the sports community.
- Financial Transparency and Accountability: Financial transparency and accountability in sports law are essential for maintaining the integrity of sports competitions. Financial transparency fights against financial doping and excessive spending by enforcing regulations and promoting responsible financial management among teams and leagues.
- Anti-Doping and Ensuring Clean Competition: Anti-doping and ensuring clean competition are vital components of sports law, which aims to maintain fair play. Sports law enforces anti-doping regulations, conducts drug tests, and imposes sanctions for violations, ensuring all athletes compete on an even footing.
- Gender Equality and Anti-Discrimination: Gender equality and anti-discrimination are cornerstone principles of sports law, advocating for the equal treatment of all athletes, regardless of gender, race, religion, or sexual orientation. The principles aim to eliminate discriminatory practices and promote inclusivity and fairness in sports.
How Is Liability Established In Cases Of Sports-Related Injuries?
Liability established in cases of sports-related injuries through a detailed legal framework. Coaches, facility owners, and participants owe a duty of care, which is fundamental to negligence law within sports law. The injured party must demonstrate that the defendant failed to meet the expected standard of care. Sports law requires that failing to meet the standard directly causes injury for establishing liability. The foreseeability of the injury plays a critical role in determining liability in sports law, underscoring the importance of preventive measures.
The critical regulations ensuring the well-being and safety of athletes, reflecting the paramount importance of health considerations in sports, underline sports law’s emphasis on the significant responsibilities of coaches and trainers in preventing sports-related injuries. The responsibilities include ensuring safe facilities, providing competent supervision, and delivering informed instruction. Special attention to participants with unique needs is mandated under sports law, highlighting inclusivity and safety. Sports law applies a higher standard for establishing negligence in professional sports, reflecting the competitive nature. Sports law’s approach balances the inherent risks of sports activities with the imperative to safeguard athletes’ health and safety.
The legal precedents and regulations under sports law exemplify the commitment to athlete well-being and safety. Each case in sports law is evaluated on specifics, considering the duties and standards of care. Sports law thus plays a pivotal role in shaping the safety protocols and ethical considerations in sports activities. The framework of sports law serves as a cornerstone for ensuring that the health and safety of athletes are always prioritized, reflecting the paramount importance of health considerations in sports.
Does Insurance Law Include Athletes To Cover Them For Injuries?
Yes, insurance law includes athletes to cover them for injuries, integrating various types of insurance policies specifically designed for the sports industry. The legal provision is critical in ensuring athletes’ well-being and financial security, highlighting the pivotal role of sports law in athlete protection.
Sports law recognizes the necessity of insurance for athletes, offering policies like temporary total disability (TTD), permanent total disability (PTD), and accidental death and dismemberment (AD&D). The policies address the distinct risks associated with sports, providing coverage for medical expenses, loss of earnings, and rehabilitation costs due to sports-related injuries.
The integration of insurance within sports law extends to contractual obligations, requiring teams and sports organizations to secure coverage for their athletes. The insurance law approach protects the athletes and the financial interests of the organizations involved, underlining the comprehensive coverage offered by sports law.
Insurance law encompasses a range of policies to safeguard athletes against injuries, underscoring the importance of financial and medical protection within sports law. Detailed insurance coverage allows athletes to concentrate on recovery and performance, providing them with support in case of injury.
What Is The Role Of Contract Law In Professional Sports?
The role of contract law in professional sports is to establish legally binding agreements that dictate the rights and responsibilities of all parties involved. Sports law ensures clarity, fairness, and protection for athletes, teams, leagues, and other stakeholders through contract law, facilitating the orderly conduct of sports at a professional level.
The contractual frameworks that govern the relationships between athletes, teams, and other stakeholders, serving as the structural basis for professional sports engagements, are crucial for the industry’s integrity. Player contracts, for instance, detail compensation, terms, performance expectations, and intellectual property rights, laying out the conditions of the athlete-team relationship in sports law. League contracts set the rules for revenue sharing, salary caps, and draft processes, directly influencing the league’s competitive balance and operational aspects.
Collective bargaining agreements between athletes’ unions and leagues establish standards for minimum salaries, free agency rules, and grievance procedures. The agreements under sports law are vital for maintaining a fair and equitable professional sports environment, ensuring the interests of players and organizations are adequately protected.
Contract law serves as an enforcement mechanism in professional sports, providing a legal basis for resolving disputes arising from complex relationships. Player challenges to suspensions, league investigations into tampering, or disputes over the use of an athlete’s likeness demonstrate how sports law, through contract law, provides a pathway to justice and resolution.
Contract law is paramount in professional sports. The law serves as the foundation for all professional engagements and relationships. Contract law is the backbone of sports law that supports all professional sports engagements, ensuring that the sports industry operates smoothly while safeguarding the rights and interests of all parties involved.
How Does Sports Law Address Issues Of Discrimination And Equality?
Sports law addresses issues of discrimination and equality by establishing a legal framework that ensures fair treatment for all athletes. The framework comprises national and international laws that explicitly prohibit discrimination based on race, gender, religion, disability, and sexual orientation. Sports law mandates all athletes, regardless of background, receive equal opportunities and respect in their sporting environment.
The laws and policies aimed at ensuring equality, combating discrimination within sports, and addressing fundamental rights issues in sports. Sports law plays a critical role in setting the standards, requiring sports organizations to adopt policies that promote diversity and inclusion. Sports law experts work diligently to ensure the legal and policy frameworks are effectively implemented across all levels of athletic competition.
Specific sports regulations, developed under the umbrella of sports law, target discrimination directly by setting out rules against harassment, hate speech, and unequal treatment. Sports law provides the basis for discrimination and equality regulations, ensuring the law aligns with broader legal principles of fairness and equality. Sports law specialists are pivotal in crafting and enforcing the regulations, holding sports entities accountable for breaches.
Contractual provisions within athlete contracts include anti-discrimination clauses, a direct outcome of sports law’s influence. Sports law advises on including clauses to protect athletes from discrimination and establish a clear recourse in the event of violations. The provisions testify to sports law’s commitment to creating a safe and equitable sporting environment.
Sports law outlines procedures for reporting, investigating, and addressing discrimination, ensuring victims have a clear path to seek redress. Establishing the mechanisms underlines sports law’s role in fostering accountability and transparency within sports organizations. Sports law professionals are essential in managing the processes and ensuring the law is conducted with fairness and integrity.
Ongoing efforts to address discrimination in sports, guided by sports law, include developing educational programs and strengthening reporting systems. Sports law continues to evolve, reflecting a commitment to addressing new challenges and reinforcing the principles of equality and non-discrimination. Sports law ensures that the sporting world remains a domain where equity prevails through efforts.
Sports law serves as the cornerstone for combating discrimination and promoting equality in sports. The law’s comprehensive approach, encompassing legal frameworks, regulations, and policies, ensures sports remain accessible and fair for everyone.
How Is Intellectual Property Protected In The Sports Industry?
Intellectual property is protected in the sports industry through specific legal protections. The mechanisms include trademarks, copyrights, patents, and industrial designs. Each plays a vital role in sports law, securing the proprietary rights of stakeholders across the sports sector.
The protection mechanisms for intellectual property in sports safeguard the proprietary rights of stakeholders in the sports industry. Trademarks protect logos, team names, slogans, and distinctive branding elements, which are crucial for brand recognition and merchandising strategies in sports law. Copyrights defend creative expressions, from event broadcasts to merchandise designs, ensuring control over reproduction and distribution. Patents cover innovations in sports equipment and technology, encouraging advancements that benefit the industry. Industrial designs protect the unique appearance of sports equipment and apparel, preventing unauthorized copies.
Trademarks in sports law play a key role, granting exclusive rights to use specific logos or names, thereby preventing confusion and protecting the brand’s reputation. Copyrights offer a means to control the use and dissemination of creative works, from songs to video recordings of events. Sports law, intertwined with intellectual property law, encourages the development of innovative sports equipment by offering inventors exclusive rights through patents. Industrial designs ensure the aesthetic elements of sports products remain protected, supporting brand identity and consumer appeal.
Stakeholders in sports law utilize IP protections to generate revenue, maintain brand identity, and foster innovation. Licensing agreements are critical for monetizing intellectual property, creating lucrative sports law jobs, and linking legal expertise directly with the sports industry’s economic aspects. The strategic use of IP rights underscores the symbiotic relationship between sports law and industry growth, ensuring a dynamic environment for stakeholders.
The comprehensive protection of intellectual property that falls under sports law ensures stakeholders innovate, compete, and thrive. The sports industry continues to evolve through trademarks, copyrights, patents, and designs bolstered by legal frameworks that support creativity, technological advancement, and brand integrity. The meticulous approach to IP protection is pivotal, sustaining the vibrancy and commercial success of the sports sector.
What Legal Considerations Are Relevant For Sports Sponsorship And Endorsements?
Legal considerations are relevant for navigating the complex landscape of sports sponsorships and endorsements, ensuring athletes and brands are protected under sports law. The considerations span various legal domains, highlighting the need for thorough contractual agreements and adherence to applicable laws.
Legal considerations for sponsorships and endorsements start with contract law, emphasizing the importance of clear, comprehensive contracts. The documents must meticulously outline the rights and obligations of both parties, detailing the scope of services, compensation methods, and conditions for termination. The precision under sports law prevents misunderstandings and protects both parties interests.
Intellectual property rights are crucial in sports law, particularly in sponsorships and endorsements. Contracts must specify which rights are granted to the sponsor for using an athlete’s image, name, and likeness for promotional purposes. The extent of the rights, including territorial limitations and exclusivity, must be carefully defined to respect the athlete’s image and the brand’s marketing needs.
Disclosure and truth in advertising principles require athletes to disclose their relationships with sponsors transparently, ensuring that endorsements are not misleading. Sports law mandates honesty in advertising, protecting consumers, and maintaining the credibility of athlete endorsements.
Antitrust considerations under sports law examine how exclusive endorsement deals affect competition within the marketplace. The deals are scrutinized to prevent unfair competitive advantages and ensure a level playing field in sports and related commercial activities.
Morals clauses are increasingly common in sponsorship contracts, allowing brands to sever ties if an athlete’s behavior adversely affects the brand’s reputation. The clauses are vital in sports law to maintain the ethical standards and public image of athletes and sponsors.
Tax implications of sponsorships and endorsements are another critical legal consideration, with athletes needing to understand the tax responsibilities associated with their income from such deals. Sports law intersects with tax law to ensure compliance and proper income reporting.
International considerations are crucial for global endorsements, requiring an understanding of differing intellectual property and advertising regulations across countries. Sports law ensures global marketing strategies comply with local laws, protecting the interests of athletes and brands internationally.
Addressing the legal considerations in sports law is fundamental for successful and lawful sports sponsorships and endorsements, safeguarding athletes’ rights and well-being while fulfilling the brands’ commercial objectives.
How Does Employment Law Relate To Professional Athletes And Sports Organisations?
Employment law relates to professional athletes and sports organizations through several nuanced interactions. Sports law encompasses traditional employment protections while acknowledging the unique aspects of athletic careers. Professional athletes, though not fitting the standard employee model, fall under sports law that adapts employment principles to their distinct environment. Collective bargaining agreements negotiated by player unions within sports law play a pivotal role in defining athletes’ working conditions and rights, superseding conventional employment statutes.
Sports law ensures that athletes receive certain employment law protections including minimum wage standards and anti-discrimination measures, tailored to the professional sports context. Another crucial aspect is workplace safety, which demands sports organizations provide secure environments, aligning with employment law under the broader umbrella of sports law. The classification of athletes as employees or independent contractors remains a contentious issue within sports law, directly impacting their rights and benefits.
Sports law addresses the unique dynamics of free agency and player mobility, starkly contrasting with other professions’ employment scenarios. Salary caps and revenue sharing, specific to sports law, further influence the bargaining power of professional athletes compared to traditional employees. Sports law, with ongoing evolution, incorporates considerations for modern challenges including mental health, data privacy, and potential exploitation of minor league athletes. The approach ensures employment law principles adapt effectively to the shifting dynamics of professional sports.
Do The Sponsorships Have Contracts?
Yes, sponsorships have contracts in professional sports. Sports law places a high premium on legal documents to ensure clarity and legality, which is fundamental for both sponsors and the entity’s support. Contracts mitigate the risk of misunderstandings and future legal disputes by delineating the rights and obligations of all involved parties. The agreements serve as a cornerstone in sports law, providing a structured framework for conducting sponsorship transactions.
Contracts in sports law elaborate on financial aspects and the scope of work required from the sponsored party. Specifications include the number of sponsorship fees, outlines of payment schedules, and the possible inclusion of performance-based incentives. The documents articulate the deliverables and expectations including displaying the sponsor’s logo and participating in promotional activities. Sports law ensures that comprehensive contracts define and protect the sponsor’s investments and the sponsored party’s commitments.
Sports law dictates sponsorship contracts address terms of duration and conditions for termination, offering security to both sponsors and sponsored parties. The contracts incorporate confidentiality clauses to safeguard sensitive marketing strategies or product innovation information. Sports law acknowledges the occurrence of smaller sponsorships based on verbal agreements and strongly discourages such arrangements. Sports law aims to prevent misunderstandings and ensure comprehensive protection for all parties advocating for written contracts.
What Are The Legalities Surrounding Doping And Anti-Doping Measures In Sports?
The legalities surrounding doping and anti-doping measures in sports are established through a comprehensive global and national regulatory framework. The framework, guided by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) and embodied in the World Anti-Doping Code, sets the standard for what constitutes doping and outlines the consequences for violations. Sports law is critical in ensuring the standards are uniformly applied and respected across all sports and countries.
The legal frameworks regulating the use of performance-enhancing substances and the associated legalities reflect the ethical and fair play considerations in sports. National Anti-Doping Organizations (NADOs) implement the WADA Code within their jurisdictions, conducting tests and managing education initiatives to combat doping. Sports law underpins the efforts, providing the legal authority to enforce anti-doping rules and impose sanctions on violators, ranging from disqualification to financial penalties.
Sports law further addresses the complexities of doping detection, due process, and the right to fair hearings for accused athletes. The provision of Therapeutic Use Exemptions (TUEs) illustrates sports law’s flexibility in accommodating athletes’ health needs while maintaining competition integrity. Legal challenges in doping involve ensuring the harmonization of anti-doping efforts globally, requiring consistent enforcement across different sporting organizations and jurisdictions.
The legalities surrounding doping and anti-doping measures in sports constitute a vital aspect of sports law to preserve the integrity of sports competitions. Sports law facilitates a competitive environment that values ethics, health, and fair play above all by establishing clear regulations, enforcing compliance, and providing mechanisms for fair adjudication.
How Are Broadcasting Rights Regulated Within Sports Law?

Broadcasting rights are regulated within sports law through a detailed legal framework governing sports content distribution and monetization. The framework includes identifying ownership and licensing agreements and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, which are pivotal for protecting the interests of all parties involved in sports broadcasting.
The legalities surrounding the broadcasting rights of sports events reflect the commercial aspects and revenue considerations in sports. Sports law dictates the process of licensing the rights to broadcasters, outlining the geographical scope, media platforms, and duration. The regulations serve as the cornerstone for generating significant revenue streams for sports organizations and athletes, highlighting the integral role of sports law in the commercial dynamics of sports.
Sports law addresses competition concerns, ensuring that allocating broadcasting rights does not lead to anti-competitive practices. Regulatory bodies scrutinize agreements to prevent monopolies and ensure a fair market, allowing fans broad access to sporting events. Sports law ensures the distribution of broadcasting rights and fosters a competitive and diverse media landscape.
Sports law mandates certain events to be available to the wider public, balancing commercial interests with public accessibility. Regulations require broadcasters to offer major events on free-to-air channels, safeguarding fan access to important sports content. The process demonstrates how sports law navigates between maximizing commercial benefits and upholding the public’s interest in accessing sporting events.
The regulation of broadcasting rights within sports law is a multifaceted endeavor. The process involves complex negotiations backed by legal agreements, ensuring fair competition and balancing commercial profitability and public accessibility. The mechanisms of sports law play a critical role in shaping the broadcasting landscape of the sports industry, ensuring that the law operates smoothly while catering to the needs of all stakeholders involved.
How Are Dispute Resolution And Arbitration Handled In Sports Law?
Dispute resolution and arbitration are handled in sports law through specific, structured mechanisms tailored to the sports industry. Dispute resolution in sports law encompasses negotiation, mediation, and conciliation to facilitate amicable settlements outside the court. The approaches prioritize confidentiality, reduce costs, and empower parties to forge mutually beneficial solutions. Sports law ensures that disagreements are resolved efficiently through direct dialogue or with the help of a neutral facilitator, maintaining the integrity and reputation of sports entities.
Arbitration in sports law is a formal method in which a neutral arbitrator delivers a binding decision after evaluating arguments from both sides. The process is celebrated for rapid resolution capabilities, sports law expertise, and decisions’ conclusive nature. Arbitrators, experts in sports law, provide informed resolutions that reflect the sector’s complexities. Arbitration is a cornerstone of sports law, offering a timely, knowledgeable, and final resolution method pivotal for maintaining seamless sports activities and relationships.
Sports governing bodies further reinforce the use of dispute resolution and arbitration through established internal procedures. The procedures mandate attempts at mediation or arbitration before any litigation, embedding the practices firmly within the framework of sports law. Sports law facilitates a more streamlined, specialized approach to conflict resolution by prioritizing mediation and arbitration, tailored to the unique needs and dynamics of the sports world.
How Does Sports Law Apply To Amateur Athletes Compared To Professional Athletes?
Sports law applies to amateur athletes differently compared to professional athletes, focusing on distinct areas of interest and regulation. Sports law, when applied to amateur athletes, primarily addresses issues including eligibility, academic standing, and adherence to the rules of governing bodies, emphasizing education, development, and fair play. The regulations ensure that amateur athletes maintain their status while potentially receiving benefits like scholarships without direct payment for athletic participation.
Sports law, in contrast, revolves around compensation, contracts, and career management for professional athletes, reflecting the commercial aspects of professional sports. Professional athletes negotiate over salaries, bonuses, and endorsement deals, with contracts meticulously outlining the financial arrangements and rights. Sports law provides a structure for professional athletes to manage their careers, protect their rights, and resolve disputes, emphasizing the need for specialized legal representation to handle intricate matters.
Recent changes, particularly the introduction of Name, Image, and Likeness (NIL) laws in the United States, have started to blur the lines between amateur and professional athletes in sports law. The changes allow amateur athletes to profit from their personal brands, introducing new legal considerations and opportunities. Sports law continues to evolve to accommodate the shifts, ensuring that amateur and professional athletes navigate the legal complexities of their respective sports effectively.
How Do International Sports Laws Interact With National Legislation?
International law interacts with national legislation through various mechanisms in the field of sports law. Establishing the US Olympic Committee, governed by the Ted Stevens Olympic and Amateur Sports Act, showcases the interaction in the United States. Sports law in the United States incorporates international standards by creating federally chartered, non-profit organizations that adhere to global Olympic guidelines and the principles of international law. The United Kingdom sees sports law materialize through collaboration between UK Sport and in-house sports councils, promoting sports guided by national legislation and international expectations. UK Sport, as a statutory distributor of National Lottery funds, operates within a complex framework that aligns with international sports principles.
Sports law in China includes the 1995 Law on Physical Culture and Sports, aiming to develop and promote sports through national legislation that complies with international norms. The law emphasizes the importance of sports at the school level and establishes a dispute resolution mechanism, reflecting the global trend towards resolving sports-related disputes within a legal framework. The United Arab Emirates has aligned sports law with international standards by hosting prestigious sports events and establishing a chapter of the Court of Arbitration for Sport (CAS) through collaboration with the International Council of Arbitration for Sport (ICAS).
India’s sports law demonstrates the interaction between international and national legislation by maintaining the autonomy of sports bodies in accordance with the Olympic Charter. The Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports and various sports federations are pivotal in the process. The federations registered under the Societies Registration Act receive government aid while adhering to international sports federations’ guidelines.
The examples illustrate how international sports laws influence national legislation, ensuring that sports governance within countries aligns with global standards and practices. The multifaceted relationship between international sports laws and national legislation ensures compliance, fairness, and uniformity in the sports sector worldwide.
What Is The Importance Of Health And Safety Regulations In Sports Law?
The importance of health and safety regulations in sports law is to safeguard athletes’ well-being, minimize injury risks, and ensure fair play. The regulations are foundational in maintaining a safe environment for competition and practice, highlighting the prioritization of athlete health.
The critical regulations ensuring the well-being and safety of athletes reflect the paramount importance of health considerations in sports. The guidelines dictate equipment standards, playing field conditions, and proper medical protocols for injuries like concussions. Sports law, setting the standards, plays a crucial role in protecting athletes from preventable harm.
Health and safety regulations address overtraining and doping, establishing rest periods, training limits, and rigorous drug testing. The comprehensive approach under sports law ensures that competitions are won on skill and hard work, not on an athlete’s capacity to endure unsafe practices or artificially enhance performance.
The duty of care mandated by sports law obliges organizations to create reasonably safe environments for athletes. The legal obligation encompasses everything from the design of protective gear to the protocols for handling injuries, underlining the extensive scope of health and safety regulations in sports.
Our understanding of sports injuries evolves, as does the framework of health and safety regulations within sports law. The ongoing development is essential for adapting to new research and technology, further enhancing the protection afforded to athletes across all levels of competition.
How Do Transfer Regulations Impact Players And Teams In Professional Sports?
Transfer regulations impact players and teams in professional sports by dictating the terms of player movement and financial transactions. The rules limit players’ mobility, affect their career development, and alter the bargaining power between athletes and clubs. Transfer regulations influence teams’ financial management, squad building strategies, and competitive balance, creating a multifaceted impact on the sports industry through the lens of sports law.
The ethical dilemmas and moral considerations in sports law address value-based concerns in sports activities and governance. Transfer regulations raise questions of fairness, investment recovery, and the potential exploitation of players, especially younger or less established ones. Teams must help manage finances responsibly while striving to build competitive squads, leading to inflated transfer fees and financial disparities in the market.
Ethical concerns including fairness versus investment, exploitation versus opportunity, and financial disparity versus meritocracy are central to the debate on transfer regulations. Practices like third-party ownership, the undervaluation of players from developing countries, and the burdens of high transfer fees illustrate the complex ethical landscape within sports law.
The professional sports community, guided by sports law, continues seeking solutions that balance player freedom, fair compensation for teams, and maintaining competitive integrity. Proposals include standardized contract regulations, transfer fee caps, and enhanced development and solidarity payments, aiming to create a more equitable and sustainable environment for all parties involved in sports.
What Are The Ethical Considerations And Challenges In Sports Law?
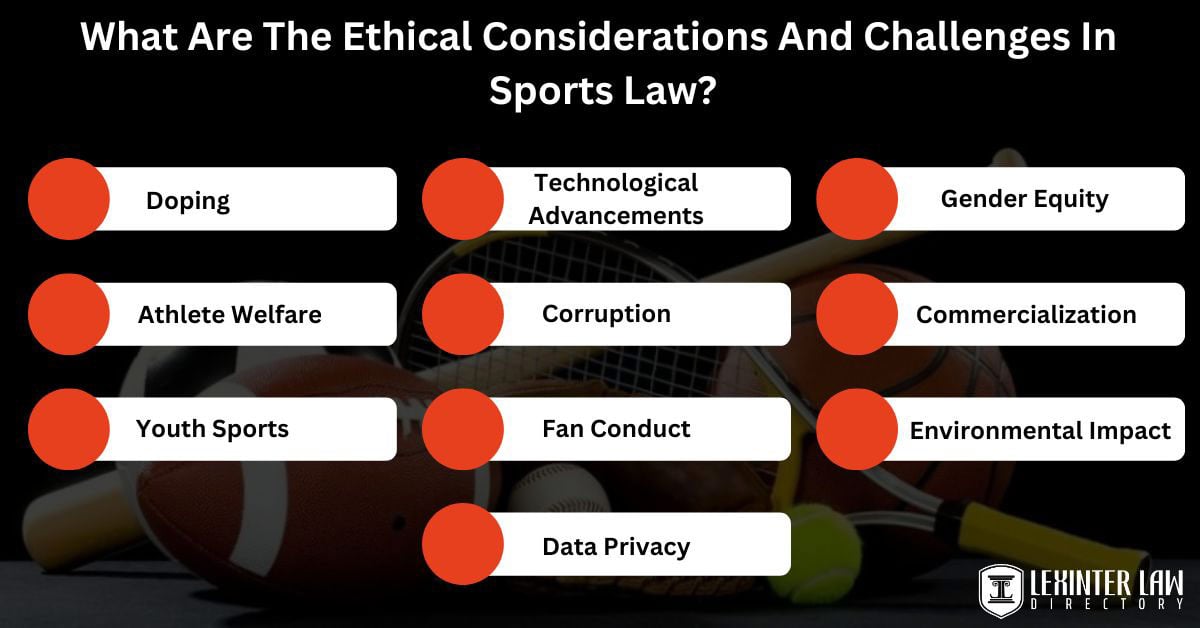
The ethical considerations and challenges in sports law are listed below.
- Doping: Ethical considerations in sports law involve regulating substance use to ensure athlete safety and competition fairness. Doping regulations balance medical treatment privacy with the need for a level playing field via therapeutic use exemptions.
- Technological Advancements: Sports law addresses the challenges of fair competition when disparities in access to technology or data insights exist among athletes or teams. The process includes the regulation of performance-enhancing technology and advanced biomechanical analysis.
- Gender Equity: Sports law addresses historical imbalances in funding, resources, and media coverage between men’s and women’s sports. Gender equity ensures equal opportunities and resources for athletes of all genders.
- Athlete Welfare: Balancing competitive demands with athlete safety is a critical challenge in sports law. Protocols for training intensity and concussion management prioritize athletes’ long-term health and well-being.
- Corruption: Sports law combats corruption to uphold sports integrity and fair competition. The efforts prevent match-fixing, bribery, and financial misconduct within sports organizations.
- Commercialization: Ethical challenges in sports law include balancing financial interests with the principles of fair play and sportsmanship. Regulations are in place to ensure sponsorship deals and advertising do not undermine competition integrity.
- Youth Sports: Youth sports of sports law emphasizes creating a developmentally appropriate sports experience for young athletes by regulating playing time and specialization. The focus is on participation, skill development, and sportsmanship, aiming to foster a positive sports culture.
- Fan Conduct: Sports law addresses fan behavior issues like harassment, violence, and discrimination. Implementing security measures and promoting respectful behavior are crucial for maintaining a safe sports environment.
- Environmental Impact: Sports law considers the environmental footprint of sporting events, promoting sustainable practices. Efforts include minimizing waste, maximizing energy efficiency, and responsible resource management.
- Data Privacy: Balancing athlete data for performance analysis with privacy rights poses a challenge in sports law. Informed consent and data security measures protect athletes’ personal information while enabling performance optimization.
How Are Immigration And Visa Issues Handled For International Athletes?
Immigration and visa issues are handled for international athletes through specific visa categories like P-1A and O-1, which cater to their unique needs. The categories are defined within the broader framework of sports law and immigration policy. International athletes demonstrate their visa eligibility through internationally recognized performance or extraordinary ability in their sport. Sports law professionals assist in the application process to ensure compliance with all requirements.
The P-1A visa allows athletes to stay in the United States for up to 5 years, with the possibility of renewal, depending on the length of their contract. The visa is designed for athletes who perform at an internationally recognized level or participate in a team sport with significant revenue or structure. Sports law emphasizes the importance of proving international recognition through various means including awards, rankings, or significant sports contributions.
The O-1 visa, designed for athletes with extraordinary abilities, offers a 3-year stay in the United States, with extensions available based on contractual commitments. Sports law identifies the O-1 visa as suitable for individuals who have reached the pinnacle of their careers. The category requires substantial evidence of the athlete’s achievements and recognition in the sport.
Athletes who are not employed in the United States consider a B-1 visa for competition purposes, highlighting the flexibility within sports law for different athletic endeavors. The visa is appropriate for athletes competing for prize money without the intention of long-term employment in the U.S. Sports law experts help navigate the criteria, ensuring athletes meet the necessary standards for the classification.
The B-2 visa, conversely, accommodates amateur athletes participating in competitions or social events, further illustrating the versatility of sports law in addressing various athlete needs. The B-2 visa stresses the importance of non-professional participation, allowing athletes to engage in sports activities without remuneration beyond expense allowances.
Sports law thus plays a crucial role in guiding international athletes through the U.S. immigration process, ensuring that the specific visas applied for align with the athletes’ professional status and the nature of their competition. The legal framework provides a structured path for athletes to compete internationally while adhering to U.S. immigration policies.
Do Athletes Need A Visa To Play Abroad?
Yes, athletes need a visa to play abroad. Sports law mandates specific visas like B-1, P-1, and O-1 for athletes’ international activities in the United States. The visas serve the diverse needs of professional athletes, amateur athletes, and individuals recognized for their extraordinary abilities, ensuring their global sports participation complies with legal standards.
Athletes’ obtaining entry visas typically involves the coordination of their representing countries or clubs. The collaborative effort simplifies acquiring the necessary travel documents, with host countries issuing visas that cover the event’s duration. Sports law facilitates the streamlined process, allowing for smoother international sports engagements.
Understanding the destination country’s visa requirements is crucial for athletes and sports professionals planning to compete abroad. Early familiarization with the requirements ensures uninterrupted participation in sports activities. Athletes are advised to seek guidance from sports law experts or immigration attorneys to successfully navigate the complex landscape of international sports visa or work permit requirements.
How Does Sports Law Address The Use Of Performance-Enhancing Substances?
Sports law addresses the use of performance-enhancing substances through a well-organized and rigorous framework. The framework involves international bodies like the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA), which sets a global code delineating prohibited substances, testing procedures, and sanctions. National Anti-Doping Organizations (NADOs) within each country implement the code, conducting testing programs to ensure athletes comply with the international standards.
Testing and doping control are central to sports law’s approach to maintaining fairness and integrity in sports. Athletes are subjected to both in-competition and out-of-competition testing to screen for banned substances. The process involves accredited laboratories collecting and analyzing urine and blood samples. Doping control officers oversee the collection process, ensuring the samples are handled properly to maintain the chain of custody and the testing’s fairness.
Sanctions and consequences for doping violations under sports law are severe and aim to deter athletes from using banned substances. Athletes found guilty of doping face disqualification from competitions, forfeiture of medals, and suspension from sport for a defined period. Violations leading to lifetime bans highlight the rigorous stance of sports law on doping, emphasizing the commitment to maintaining integrity and fairness in sports competitions.
Therapeutic Use Exemptions (TUEs) provide a legal avenue for athletes with genuine medical conditions to use medications that fall under the prohibited list. Athletes seeking a Therapeutic Use Exemption (TUE) are required to present detailed medical documentation. The documentation must prove the necessity of the specified medication, confirming the document does not provide an unfair advantage in competition. The aspect of sports law recognizes the health needs of athletes while maintaining a level playing field.
Education and awareness programs are pivotal in sports law’s strategy against the use of performance-enhancing substances. Governing bodies and anti-doping agencies conduct programs to inform athletes, coaches, and support personnel about the dangers and consequences of doping. The agencies aim to cultivate a culture of clean sports by highlighting the importance of fair play and the ethical principles underlying sports competition.
How Is Governance Structured In Sports Organisations, And What Legal Issues Arise?
Governance in sports organizations is structured through membership-based, hierarchical, and hybrid models, each with specific sports law implications. The membership-based approach promotes democratic decision-making but leads to legal issues with fair representation and susceptibility to special interest influences. Hierarchical structures enable efficient governance but risk centralizing power too much, possibly neglecting the broader community’s needs. Hybrid models attempt to balance the aspects but must carefully navigate the legal complexities of combining different governance methods.
Sports law in membership-based models addresses the need for fair representation and protection against special interest domination. Legal challenges in hierarchical structures revolve around power concentration and ensuring responsiveness to member needs. Hybrid governance must navigate the complex terrain of balancing authority with member engagement, leading to unique legal considerations.
Legal issues commonly encountered across the governance structures include financial mismanagement, with sports law providing frameworks for accountability and transparency. Doping and performance-enhancing drugs pose significant challenges, requiring robust anti-doping regulations and protections for athlete rights. Discrimination and harassment issues necessitate legal obligations for safe and inclusive environments, while competition manipulation like match-fixing demands strict legal deterrents.
Globalization introduces complex legal landscapes for international sports organizations, necessitating adaptable sports law frameworks. Technological advancements bring new challenges, including data privacy and the regulation of emerging domains like esports. Effective governance in sports, thus, requires a comprehensive understanding of various legal frameworks to uphold the integrity of the game and safeguard the interests of all stakeholders.
What Is The Legal Framework Surrounding Sports Betting And Gambling?
The legal framework surrounding sports betting and gambling varies by individual countries, states, or provinces, lacking a universal standard. Each jurisdiction independently determines the regulations for sports betting and gambling activities, influenced by its own legal, cultural, and social norms. The decentralized approach, guided by sports law, results in a diverse global landscape of sports betting legality and regulation.
The regulations governing sports betting and gambling activities address the legal implications of betting activities related to sports events. The rules have led jurisdictions to impose strict restrictions or outright bans on sports betting due to concerns over gambling addiction, potential match-fixing, and the involvement of organized crime. Sports law in various areas has reflected these concerns, aiming to protect the integrity of sports competitions and the public’s welfare. The emphasis has been on preventing the negative consequences associated with sports betting.
The legal landscape of sports betting is undergoing significant changes, with a trend toward legalization and regulation. The shift in sports law is driven by increased demand from bettors, the potential for tax revenue generation, and a desire to regulate previously uncontrolled black-market activities. Changes in sports law regulations seek to balance economic benefits with the need for consumer protection and the integrity of sports events.
The 2018 decision by the Supreme Court in the United States to overturn a federal ban on sports betting resulted in a fragmented legal landscape, with more than 30 states legalizing some form of sports betting. Canada similarly legalized single-event sports betting in 2021, allowing provinces to regulate the activity. Europe presents a varied picture, with countries like the United Kingdom boasting a well-established, regulated sports betting market. International sports law, including IOC regulations, generally prohibits athletes and officials from betting on Olympic events, emphasizing the global effort to maintain sports integrity.
Legal sports betting encompasses retail betting at physical locations and online betting through licensed operators’ websites or apps. Sports law outlines the legal implications of betting activities, including age restrictions, licensing requirements, taxation, and integrity measures to combat match-fixing and insider trading. The regulations are crucial for safeguarding the fairness of sports competitions and ensuring responsible gambling practices.
The legal framework for sports betting and gambling is complex and constantly evolving, influenced by technological advancements, shifts in society’s attitudes towards gambling, and economic factors. Sports law is vital in defining the regulations, emphasizing the need for individuals to grasp the jurisdiction’s specific legal nuances. The knowledge is essential for responsibly and legally navigating the sports betting landscape.
How Does Child Protection And Welfare Integrate Into Sports Law Policies?
Child protection and welfare are integrated into sports law policies through comprehensive strategies that ensure the safety and well-being of young athletes. The policies create a framework within sports organizations to address various aspects of child welfare proactively.
One key area in sports law involves setting minimum age requirements for participation in competitions or training programs. The policy is designed to protect young athletes from the physical and mental strains of early, intense sports specialization, ensuring their engagement in sports is appropriate for their developmental stage.
Background checks for coaches, trainers, and other staff working directly with children are another critical component. Background checks aim to prevent individuals with a history of harmful behavior from being in positions that endanger the welfare of young participants. Sports law mandates preventive measures to minimize the risk of abuse within sports settings.
Reporting obligations are integral to sports law policies on child protection. Coaches, staff, and observers are required to report any signs of abuse, neglect, or exploitation they witness. The proactive approach helps identify potential issues early, ensuring immediate and appropriate interventions.
Safeguarding policies further detail the codes of conduct for interactions between adults and children in sports contexts. Safeguarding policies outline expected behaviors, reporting procedures for concerns, and training on child protection issues for all involved in youth sports. The sports law’s aim is to promote a safe and positive environment for all young athletes.
Educational sports law programs for athletes, parents, and coaches on child protection issues raise awareness about the importance of safeguarding children in sports. The programs empower young athletes to recognize and report inappropriate behavior, fostering a culture of openness and safety.
Sports law incorporates specific dispute resolution mechanisms to handle concerns related to child protection. The process includes internal review processes within sports organizations or referral to independent bodies for investigation and resolution. The focus is on ensuring that all complaints are taken seriously and addressed effectively.
Integrating specific dispute resolution mechanisms, safeguarding policies, and educational programs into sports law policies demonstrates organizations’ commitment to child welfare. The approach ensures a sporting environment that is both physically safe and supportive of children’s rights and development, showcasing a dedication to nurturing young athletes in a secure and positive setting.
How Does Sports Law Regulate Fan Interactions And Behaviours?
Sports law regulates fan interactions and behaviors through a comprehensive approach that includes preventative measures, reactive responses, and collaborative initiatives. The legal framework aims to maintain a safe and enjoyable environment at sporting events, addressing various aspects of fan conduct.
Preventative measures under sports law involve establishing stadium codes of conduct that detail acceptable and unacceptable fan behaviors including prohibiting violence and public intoxication. Security measures, including the presence of personnel and surveillance cameras, deter disruptive behavior. Alcohol policies at venues limit consumption to prevent alcohol-related incidents. Ticket sales strategies play a role, with fan identification measures in place to manage crowd control and enhance safety.
Reactive responses are implemented when fans breach established conduct codes. Security staff eject fans found violating the rules of the event. More severe or repeated offenses lead to stadium bans or, in extreme cases, criminal charges, emphasizing the legal consequences including actions within the framework of sports law.
Collaborative efforts enhance the effectiveness of sports law in regulating fan behavior. Fan education programs, developed in partnership with law enforcement and sports organizations, promote awareness of acceptable conduct. Community engagement initiatives further support a culture of respect and sportsmanship among fans.
Challenges in regulating fan interactions include balancing security measures with ensuring a positive fan experience, differentiating between freedom of speech and hate speech, and adapting regulations to accommodate cultural differences in international sporting events. The complexities highlight the nuanced role of sports law in navigating the legal and ethical landscape of fan conduct at global sporting events.
Sports law significantly influences the atmosphere of sporting events addressing components including preventative measures, reactive responses, and collaborative initiatives. The legal framework ensures safety and enjoyment for all participants, promoting sportsmanship and respect across various sports settings.
What Legal Implications Arise From Commercialisation And Monetisation In Sports?
Legal implications arise from commercialization and monetization in sports through legal frameworks designed to navigate conflicts between financial gains and sports integrity. The regulations encompass a range of laws, including antitrust, labor, data privacy, and intellectual property laws. Each set of sports laws aims to balance economic interests with maintaining fair play and safeguarding athlete well-being within the sports industry.
The legal implications arising from the commercialization and monetization activities in sports, reflecting the economic dimensions of sports, are multifaceted. Antitrust laws of sports law seek to prevent monopolistic practices that harm competition, implementing mechanisms like salary caps and revenue sharing to ensure competitive balance. Labor laws and collective bargaining agreements are crucial for protecting athletes from exploitation and addressing issues related to training hours, rest periods, and fair compensation.
The legal landscape surrounding data privacy and image rights adapts to technological advancements that enable the collection of vast amounts of athlete data. Regulations, within the framework of sports law, are being crafted to ensure that athletes’ privacy is respected and that athletes retain some control over the commercial use of their data and likeness. Intellectual property laws significantly generate revenue through licensing deals for logos, team names, and broadcasting rights, necessitating a balance between protecting the assets and ensuring access for fans.
The pressure to succeed in a highly commercialized sports environment leads to unethical practices like doping. Sports law encompasses anti-doping regulations and criminal laws to combat doping, emphasizing the need for integrity in sporting competitions. The framework surrounding sports commercialization is complex, requiring ongoing adjustments to align economic growth with ethical sportsmanship and athlete protection.
How Does Sports Law Treat Issues Of Privacy And Publicity In The Athletic Community?
Sports law treats issues of privacy and publicity in the athletic community by carefully balancing athletes’ personal rights with their public personas. The legal framework ensures that athletes’ private lives are protected, allowing them to capitalize on their fame.
The right of privacy within sports law shields athletes from unwarranted public scrutiny, protecting personal data including medical records and private communications. Athletes, through sports law, retain control over the dissemination of sensitive personal information, safeguarding their privacy from invasive public and media attention.
Sports law upholds an athlete’s right of publicity on the publicity front, which includes control over the commercial use of their name, image, likeness, and other identifiable features. The aspect of sports law prevents unauthorized commercial exploitation, allowing athletes to secure endorsement deals and other commercial opportunities that properly compensate them for the use of their persona.
Sports law firms play a pivotal role in the context, offering expertise to navigate the complexities of privacy and publicity rights. The firms help athletes and sports organizations understand their legal standings and obligations, ensuring compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Commercial use versus editorial coverage is a significant distinction made within sports law. News outlets freely use athletes’ images for reporting purposes without consent, but commercial use requires explicit permission to protect athletes from unauthorized endorsements.
League and team regulations, detailed in collective bargaining agreements, further delineate the parameters for using athletes’ images. The internal sports law rules specify conditions for marketing campaigns or outline revenue-sharing models from the commercial use of athlete likenesses, such as in video games or trading cards.
The variation in state versus federal laws concerning publicity rights complicates the legal landscape. Sports law firms adeptly manage these differences, ensuring athletes’ rights are uniformly protected across jurisdictions.
The rise of social media has introduced new challenges, blurring the lines between public and private spheres. Athletes who share personal life aspects online must navigate the implications of their online presence for their privacy and publicity rights under sports law.
Notable legal cases including Spud Webb’s lawsuit against a trading card company and Joe Namath’s against an advertising company, have helped define and enforce athletes’ rights, establishing important precedents in sports law.
Sports law provides a comprehensive framework that respects and protects athletes’ privacy and publicity rights, balancing their need for personal privacy with the opportunities and demands of their public and commercial identities.
What Is A Sports Law Degree?
A sports law degree is an educational qualification specializing in sports and athletics laws. The degree covers various legal issues in sports, including contracts, antitrust, labor law, and intellectual property rights. Students pursuing a sports law degree learn to navigate the complex legal landscape of the sports industry. Graduates pursue careers as sports lawyers, advising athletes, sports organizations, and teams on legal matters.
Earning a sports law degree requires 2 to 3 years of advanced study beyond an undergraduate degree. Programs that integrate sports law with business or management courses are available, offering a dual focus. The approach is designed to give students a thorough understanding of the legal frameworks and the commercial aspects governing the sports industry. The comprehensive programs equip future professionals with the insights and skills to navigate the complex intersections between law, business, and sports.
The curriculum of a sports law degree typically includes courses on sports governance, ethics in sports, and the business aspects of sports. The comprehensive education prepares students to address the unique challenges faced by professionals in the sports sector. A sports law degree equips individuals with the skills to negotiate contracts, manage sports-related litigation, and ensure compliance with regulations.
The significance of a sports law degree lies in the capacity to equip future sports lawyers with essential skills for navigating complex legal issues in the sports industry. Graduates pursue careers as sports lawyers, collaborating with athletes, sports organizations, and governing bodies. Sports lawyers work to ensure fair play and legal compliance, playing a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of the sports world.
The role of a sports lawyer is crucial in resolving disputes, negotiating endorsements, and protecting the intellectual property of sports entities. Professionals holding a sports law degree find themselves in a prime position to advocate for fairness, integrity, and justice within the sports industry. The specialization opens doors to various career paths in legal advising, sports management, and policy development for sports organizations.
A sports law degree offers a unique blend of legal education and sports industry insight. The degree is essential for individuals aspiring to navigate the legal complexities of the sports world, ensuring ethical conduct and legal compliance in all sports-related activities.
How To Get Into Sports Law?

To get into sports and become a sports lawyer, aspiring individuals must follow the 8 steps listed below.
- Bachelor’s Degree in Sports Law Career. Students aiming for a career in sports law must pursue degrees in relevant fields such as Political Science, Criminal Justice, or Business. Enhancing their academic journey with courses in Sports Management, Marketing, and Communications is crucial for foundational knowledge in sports law.
- Core Skills Development in Sports Law. Aspiring sports lawyers must focus on honing critical skills essential for the field, including advanced critical thinking, comprehensive research, adept writing, and effective communication. The core skills are indispensable for navigating the complexities of sports law.
- Gaining Experience in Sports Law. Engaging in internships or volunteer work within sports entities or law firms provides invaluable practical experience. The step is key for aspiring sports lawyers to establish connections and understand the intricacies of sports law.
- Law School Admission Process for Sports Law. Candidates must meticulously select law schools with robust sports law programs or proximity to major sports hubs. The law schools must offer specialized sports law courses, clinics, and externship opportunities.
- Ace Law School and Pass the Bar Exam. Dedicated engagement in sports law-related courses like Contract Law, Labor Law, Intellectual Property, and Anti-Doping Regulations is essential. Participation in sports law clinics or moot court competitions prepares students for the bar exam and a career in sports law.
- LLM in Sports Law for Specialization. Considering an LLM in Sports Law after passing the bar exam offers deeper specialization opportunities. The advanced degree enhances a sports lawyer’s expertise and marketability in the sports law field, although the degree is not a compulsory step.
- Networking and Relationship Building. Active participation in industry events, conferences, and sports law association meetings is crucial for aspiring sports lawyers. The platforms offer opportunities to connect with experienced professionals, mentors, and practitioners in sports law, facilitating career guidance and job prospects.
- Career Development and Job Search. Focusing the job search on sports law firms, professional sports leagues, teams, and athlete representation agencies is crucial. Aspiring sports lawyers must tailor their resumes and cover letters to highlight their expertise and experience in sports law, ensuring continuous professional development in the legal landscape of sports.
Can An Athlete Go To Prison Violating Sports Law?
Yes, an athlete can go to prison for violating sports law if their actions constitute a criminal offense. Sports law, focusing on regulations within the sports industry, typically enforces penalties including fines, suspensions, or contract terminations for breaches of the regulations. The consequences address fair play, athlete rights, and the integrity of sports but do not directly lead to jail time.
Certain actions violating sports law include breaching criminal law and exposing athletes to the risk of imprisonment. Doping, for example, involves illegal drug possession, trafficking, or distribution, all of which are criminal offenses. Extreme acts of violence on the field surpass the boundaries of the sport’s internal regulations and are prosecuted as assault or battery under criminal law. Match-fixing and involvement in illegal gambling represent another area where sports law and criminal law intersect, with potential criminal consequences for athletes found guilty.
Athletes must recognize that while sports law violations within the confines of the sports industry do not lead to prison, the legal implications of their actions extend far beyond the sports arena. Athletes engaging in activities that violate criminal laws face the full breadth of legal consequences, including the possibility of imprisonment. The dual nature of sports law emphasizes the need for thorough legal guidance and awareness of the legal landscape both within and outside the sports industry.

